Characterization and Thermal Behaviour of Magnesium-Aluminium Layered Double Hydroxide
Keywords:
Layered double hydroxide, co-precipitation, anionic clay, thermal behaviour, nano materialAbstract
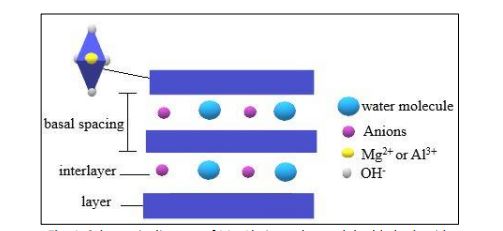
Layered double hydroxide achieved a lot of attention because it is simple, eco-friendly and easy to synthesize, involved non-toxic chemical, economical, good thermal stability with broad spectrum application. Thus, layered double hydroxide gained trust by the academician and industrial in developing layered double hydroxide studies. Thermal behaviour does influence by layered double hydroxide molar ratio therefore this study focuses on the molar ratio effect of Mg-Al nitrate LDH on the characterization and thermal behaviour properties. The divalent and trivalent cation of magnesium nitrate hexahydrate (Mg (NO3)2·6H2O) and aluminium nitrate nonahydrate (Al (NO3)3·9H2O) ratio are 2:1, 3:1 and 4:1 synthesize by co-precipitation method. The X-ray diffraction analysis shows lower molar ratio obtain high crystallinity index as aluminium concentration decreased and the crystallinity does affect the heat flow of the material in differential scanning calorimetry analysis. A typical presence of the inorganic-organic compound within the network structure of layered double hydroxide in Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The thermal stability from thermogravimetric analysis proved decomposition occurred with formation of oxide mixture in the materials network.
Downloads