Two-Phase Flow Boiling Heat Transfer Coefficient with R290 in Horizontal 3 mm Diameter Mini Channel
Keywords:
Heat transfer coefficient, asymptotic, R290, two-phase flow boiling, mini channelAbstract
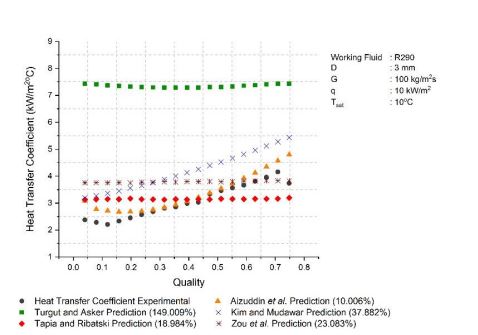
Various experiments about the heat transfer coefficient of two-phase flow boiling in a mini channel tube have been carried out. In addition to obtaining data on heat transfer coefficients experimentally, many researchers compare their experimental data and even add the data from other researchers with existing correlations. This study aims to obtain experimental data and the characteristics of the heat transfer coefficient of two-phase flow boiling of refrigerant R290 in a horizontal mini channel tube. The mass flux is varied from 50 kg/m2s - 180 kg/m2s and heat flux of 5 kW/m2 - 20 kW/m2. The test section is a stainless-steel mini channel tube with a 3 mm diameter and a length of 2 m. The experimental data obtained are then predicted with various correlations of the available heat transfer coefficients. The correlation that will be used in this study is based on the asymptotic flow model, where this model is a combination of nucleate and convective flow boiling mechanism. This paper will show the example of the comparison between the heat transfer coefficient experimental and the prediction of some correlation with the condition of mass flux 100 kg/m2s and 150 kg/m2s, and heat flux 10 kW/m2 and 15 kW/m2. The result of the heat transfer coefficient experimental data depends on the mass quality and heat flux. The value increases with increasing mass quality and decreases drastically as mass quality approaches 1. The correlation of Aizuddin et al. is the most accurate, with a deviation of 10.006% in the experiment with the condition of mass flux 100 kg/m2s and heat flux 10 kW/m2. While in the experiment with the condition of mass flux 150 kg/m2s and heat flux 15 kW/m2 has a deviation of 9.969%.
Downloads