Effect of Cerium Oxides Loaded Nitric Acid-Treated Palm Kernel Shell Biochar on Pyrolysis of High-Density Polyethylene
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/jrnn.16.1.6070Keywords:
Plastic waste, Pyrolysis, Biochar, Cerium Oxides, Fuel, HydrocarbonsAbstract
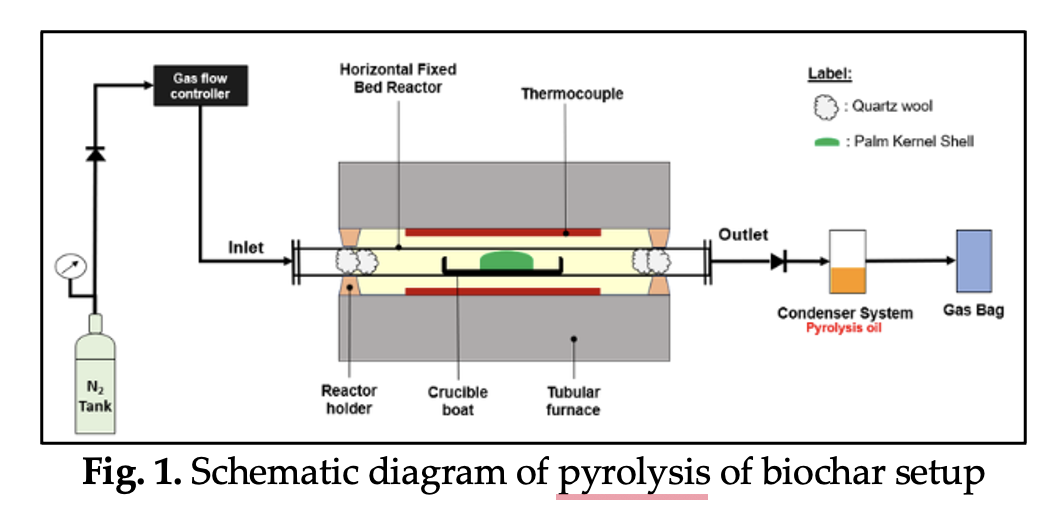
This study aims to evaluate the physicochemical properties of cerium oxides loaded nitric acid-treated palm kernel shell biochar (Ce/NA-PKSBC) and examine their catalytic performance in the pyrolysis of high-density polyethene (HDPE). The catalyst was prepared in two steps, first via pyrolysis and then the incipient wetness impregnation method, and characterised for surface morphology and textural properties. Pyrolysis was conducted at 500°C in a fixed-bed horizontal reactor, with oil product analysis performed using gas chromatography/ mass spectrometry (GC/MS). For comparison, the non-catalytic, raw PKSBC, and NA-PKSBC catalysts were also pyrolysed under the same conditions. The results indicate that the Ce/NA-PKSBC exhibited improved surface morphology and significantly enhanced textural properties compared to PKSBC, and Ce/NA-PKSBC has the highest surface area at 369.62 m2/g compared to other synthesized catalysts. For pyrolysis results, the non-catalytic achieved the highest pyrolysis oil + wax at 91% followed by NA-PKSBC (68%), PKSBC (60%), and Ce/NA-PKSBC (46%). Ce/NA-PKSBC achieved notable yields of hydrocarbons at 93.25%. These findings suggest that Ce-modified represent a viable and sustainable alternative to conventional catalysts, offering high efficiency and environmental compatibility for converting plastic waste into fuel.Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Downloads
Published
2025-08-26
How to Cite
Kui Ee, T. ., Balasundram, V., Ibrahim, N., Isha, R., Hoang, L. K. P., & Shi, S. (2025). Effect of Cerium Oxides Loaded Nitric Acid-Treated Palm Kernel Shell Biochar on Pyrolysis of High-Density Polyethylene . Journal of Research in Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 16(1), 60–70. https://doi.org/10.37934/jrnn.16.1.6070
Issue
Section
Letters














