The Optimum Percentage of Rice Husk Ash (RHA) as Partial Cement Replacement in Engineered Cementitious Composite (ECC)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/jrnn.5.2.19Keywords:
Compressive Strength Test, Engineered Cementitious Composite (ECC), Flow Table Test, Particle Size Distribution, Rice Hush Ash (RHA)Abstract
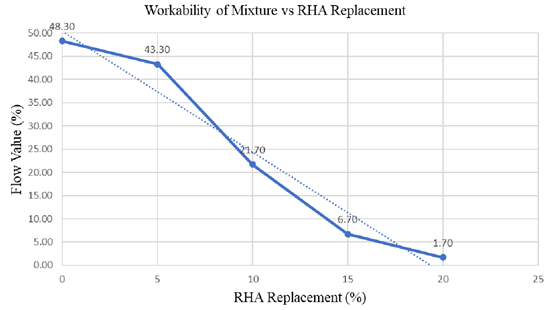
Rice Husk Ash (RHA) is a potential supplementary cementitious material (SCM) in concrete production due to their capability of pozzolanic reaction. This research study on the fineness, workability and compressive strength of the RHA incorporated into Engineered Cementitious Composites (ECC) as a cement replacement alternative hence to determine the optimum percentage of RHA to be use in the ECC mix. The mix proportional of RHA-ECC was designed with RHA as the substitution of Portland cement at various percentages by volume, including 5%, 10%, 15% and 20% respectively. Physical characterization of RHA was determined by particle size distribution test. The workability of hand mixed mortar was determined by the flow table test. A total of 45 cubes of 50×50×50 mm was prepared and cured for 7, 14 and 28 days. These hardened mortars were test with the compressive strength test to study its mechanical property. Findings showed that the workability of RHA-ECC was decreased with increasing of the amount of RHA added. The compressive strength of RHA-ECC was best at 28 days with the 10% of replacement level compared to others. This study will provide both direction and knowledge on the application of RHA as a greener and sustainable cement replacement.
Downloads