Solute Dispersion in Casson Blood Flow through an Artery with the Effect of Electric Field
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/jrnn.9.1.1334Keywords:
Blood flow, Casson fluid, Generalized dispersion model, Solute dispersion, Electric fieldAbstract
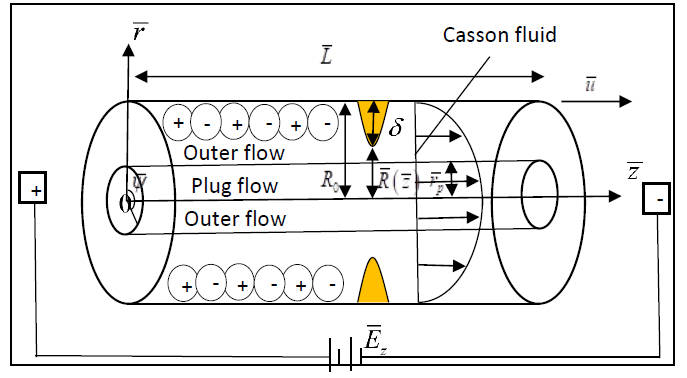
A condition of the heart or blood vessels is referred to as cardiovascular disease (CVD). When it comes to cancer, people with CVD are more likely to get it than people without it. The correlation between atherosclerosis and particular cancer subtypes, which remains even after adjusting for traditional risk factors, could contribute to this link. The motivation for this work is to analyse the steady flow of dispersion of solute in blood flow through an artery with the effect of an electric field. Blood is considered a Casson fluid model. The velocity of the Casson fluid model is determined by solving momentum and constitutive equations. The concentration of solute, dispersion function and mean concentration are obtained by using the Generalized Dispersion Model (GDM). The results are validated with the previous solution without the effects of electric field and stenosis. The results showed good conformity between the two solutions. An increase in electric field increases the velocity, steady dispersion function and mean concentration while reducing the unsteady dispersion function and dispersion function. It is observed that the solute dispersion in blood flow affects the electric field. Casson fluid is an appropriate fluid to investigate the blood velocity and transportation of the drug in blood flow to the targeted stenosed region through a very narrow artery for the treatment of arterial diseases.
Downloads