Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid Nanoparticles: Flow Rates and Gauge Sizes Influence the Droplet Surface Tension and Particle Sizing
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/jrnn.9.1.112Keywords:
Electrospray, Nanomaterials, Tate’s law, PLGAAbstract
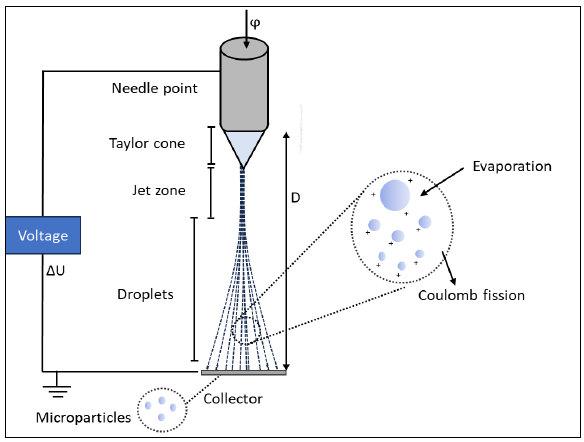
Electrospray is a novel and versatile approach to the synthesis of nanosized particles. In this paper, the effects of electrospray process parameters such as gauge size (18 G-25 G) and flow rate (0.9-1.5 ml hr-1) on droplet surface tension and electrospray particle size were evaluated. 25 mg Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) were dissolved in 100 ml acetone before being subjected to electrospray. Tate’s Law was used to calculate the surface tension while the Malvern nanosizer was used to measure the particle size. Based on Tate’s Law calculation, when the gauze size increased from 18 G-25 G, the droplet surface tension increased from 10.07 Nm-1 to 18.17 Nm-1 showing a direct pattern. At the same time, the flowrate is inversely proportional to droplet surface tension. When the flow rate increased from 0.9-1.5 ml hr-1, the droplet surface tension was reduced. This is due to the increasing ratio of vicious force and surface tension. For particle size, as surface tension increased from 10.07 Nm-1 to 18.17 Nm-1, particle size increased from 205.57 nm to 612 nm owing to the corona discharge producing larger progeny droplets that chain into smaller particles through coulomb fission as more charge is required to overcome the surface tension. In conclusion, flow rate and gauge size influenced the surface tension thus affecting the nanosized particles.
Downloads