In Silico Molecular Docking Simulation of Chromolaena Odorata Phytoconstituents Against Matrix Metalloproteinase Proteins – 9 (MMP-9)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/jrnn.7.1.16Keywords:
Chromolaena Odorata, wound healing, Matrix Metalloproteinases, molecular dockingAbstract
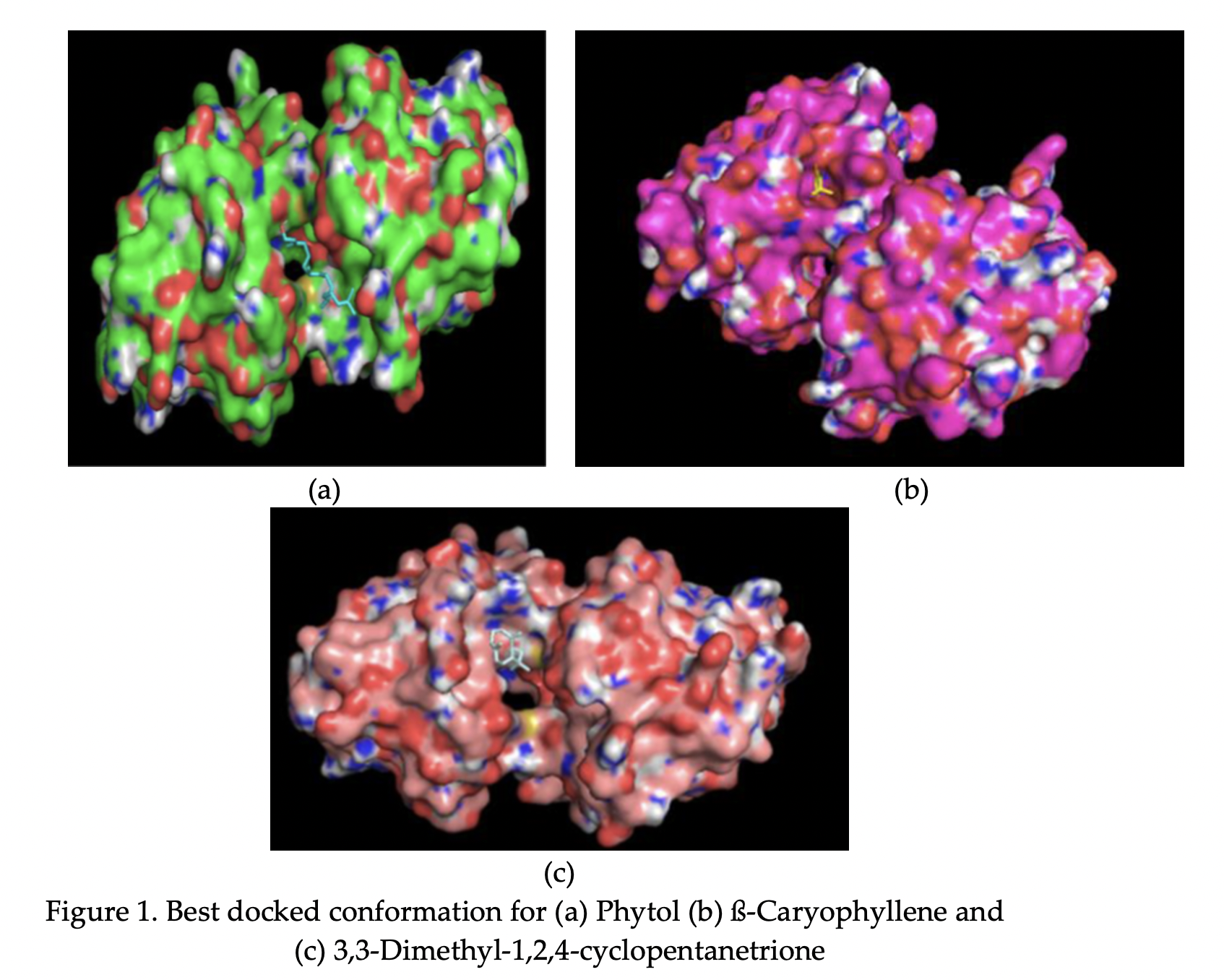
The purpose of this study is to investigate the potential ligands of Chromolaena Odorata plants which contributes to the wound healing process. The ligands involved were phytol, ß-Caryophyllene, and 3,3-Dimethyl-1,2,4-cyclopentanetrione. This work addressed molecular docking simulations between the chosen ligands and Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP) as the primary viral protein/receptor. The binding modes of the protein-ligand interactions were analysed. 9 poses of docking modes were obtained from the simulation. The ligand-receptor with the lowest interaction energy is the potential candidate for wound healing treatment. In summary, 3,3-Dimethyl-1,2,4-cyclopentanetrionehas been chosen to be the best docked complexes as it shows the lowest energy among the other ligands with value of -7.1 kcal/mol.Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Downloads
Published
2023-03-23
How to Cite
Nur Qamarina Hazian, Nur Ainun Mokhtar, Nurulbahiyah Ahmad Khairudin, & Ragheed Hussam Yousif. (2023). In Silico Molecular Docking Simulation of Chromolaena Odorata Phytoconstituents Against Matrix Metalloproteinase Proteins – 9 (MMP-9) . Journal of Research in Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 7(1), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.37934/jrnn.7.1.16
Issue
Section
Research papers














