Green Synthesis of Sodium Alginate Mediated Fluorapatite Nanoparticle via Sol-Gel Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/jrnn.2.1.3041Keywords:
Green synthesis, fluorapatite, hydroxyapatite, sol-gel, sodium alginateAbstract
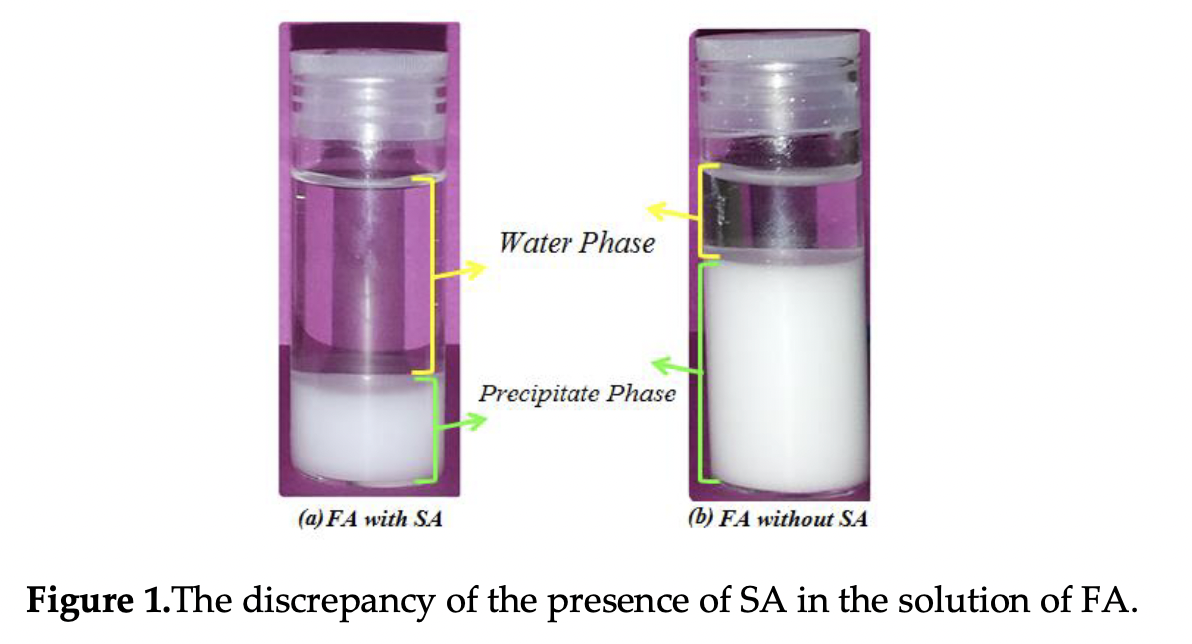
Fluorapatite (FA) can be used as a bioactive substance in the body, especially the teeth implants. The FA nanoparticle was synthesized by adding the fluorine to the structure of HA using sol–gel method and the heat treatment of 700 °C. Being low costs, eco-friendly and safer features are obvious advantages of the green synthesis of FA nanoparticles by using bio stabilizer of sodium alginate. Calcium nitrate tetrahydrate, diammonium phosphate, ammonium fluoride were used as precursors of Ca, P and F respectively with the ratio of 1:67 Ca/P. The presence of crystal structure of HA and FA investigated by the results of XRD which confirmed the substitution of hydroxyl groups with the fluorine in the crystal structure of apatite. FTIR obtained that fluorine was substituted by hydroxyl groups in the structure of fluoridated hydroxyapatite by disappearing the hydroxyl groups at 3600 cm-1 in the FA. TGA investigated the thermal stability of the nanoparticles that showed the discrepancy of weight loss for HA and FA between 600?C to 800?C. By using TEM, average sizes of 35 and 49 nm were determined for HA and FA respectively. FESEM results confirmed the shapes and distribution of particles of HA and FA in that, round like for the former and rode like for the later. The overall performance of utilizing sodium alginate (SA) as a bio-stabilizer is to obtain better precipitate which leads to having better crystallinity and smaller particle size and thermal stability remarkably improved.
Downloads
References
K. Shameli, M. Ahmad, S. D. Jazayeri, P. Shabanzadeh, H. Jahangirian, M. Mahdavi, and Y. Abdollahi. Synthesis and characterization of polyethylene glycol mediated silver nanoparticles by the green method. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2012, 13(6 ), pp. 6639-6650. doi: 10.3390/ijms13066639.
M. Ahmad, Y. T. Mei, K. Shameli, M. Z. Hussein, and J. J. Lim. Green synthesis and characterization of silver/chitosan/polyethylene glycol nanocomposites without any reducing agent. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2011, 12(8), pp. 4872-84. doi: 10.3390/ijms12084872.
K. Shameli, M. Ahmad, W. Z. W. Yunus, and N. A. Ibrahim. Synthesis and characterization of silver/talc nanocomposites using the wet chemical reduction method. Int. J. Nanomedicine., 2010, 5, 743. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S13227.
F. Namvar, S. Azizi, M. Ahmad, K. Shameli, R. Mohamad, M. Mahdavi and P. M. Tahir. Green synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using the marine Macroalgae Sargassum Muticum. Res. Chem. Intermed., 2015, 41(8), pp. 5723-30. doi: 10.1007/s11164-014-1696-4.
H. Jahangirian, M. H. S. Ismail, M. J. Haron, R. Rafiee-Moghaddam, K. Shameli and S. Hosseini. Synthesis and characterization of zeolite/Fe3O4 nanocomposite by green quick precipitation method. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct., 2013, 8.(4), pp. 1405-1413.
R. Khandanlou, M. Ahmad, H. R. Fard Masoumi, K. Shameli and M. Basri, Rapid adsorption of copper (II) and lead (II) by rice straw/Fe3O4 nanocomposite: optimization, equilibrium isotherms, and adsorption kinetics study. PloS one., 2015, 10.(3), pp. 1-19. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120264.
Z. Izadiyan, K. Shameli, M. Miyake, H. Hara, S. H. Mohd Taib and E. Rasouli, Cytotoxicity assay of plant-mediated synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles using Juglans regia green husk extract. Arab. J. Chem., 2020, 13.(1), pp. 2011-2023. doi; 10.1016/j.arabjc.2018.02.019.
R. Khandanlou, M. Ahmad, K. Shameli and K. Kalantari, Synthesis and characterization of rice straw/Fe3O4 nanocomposites by a quick precipitation method. Molecules, 2013, 18.(6), 6597-6607. doi: 10.3390/molecules18066597.
K. X. Lee, K. Shameli, Y. P. Yew, S. Y. Teow, H. Jahangirian, R. Rafiee-Moghaddam and T. J. Webster. Recent developments in the facile bio-synthesis of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and their biomedical applications. Int. J. Nanomed., 2020, 15, pp. 275-300. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S233789.
P. Shabanzadeh, N. Senu, K. Shameli, F. Ismail, A. Zamanian, and M. Mohagheghtabar. Prediction of silver nanoparticles’ diameter in montmorillonite/chitosan bionanocomposites by using artificial neural networks. Res. Chem. Intermed., 2015, 41(5), pp. 3275-3287. doi: 10.1007/s11164-013-1431-6.
P. Shabanzadeh, R. Yusof, and K. Shameli. Modeling of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles in Vitex negundo L. extract by artificial neural network. RSC Advances., 2015, 5(106), pp. 87277-87285. doi: 10.1039/C5RA11940E.
P. Shabanzadeh, N. Senu, K. Shameli and M. Mohaghegh Tabar. Artificial intelligence in numerical modeling of silver nanoparticles prepared in montmorillonite interlayer space. J. Chem., 2013, 2013, pp. 1-8. doi: 10.1155/2013/305713.
S. K. Balavandy, K. Shameli, and Z. Z. Abidin, Rapid and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles via sodium alginate media. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2015., 2015, 10.(1), 486-497.
P. Khadeeja, V. Banse and L. Ledwani. Green synthesis of nanoparticles: their advantages and disadvantages. Paper presented at the AIP conference proceedings., 2016. doi:10.1063/1.4945168.
K. Omer, G. Vural, S. Keser, I. S. Yahia, N. Bulut, T. Ates and S. Koytepe. Ce/Sm co-doped hydroxyapatites: synthesis, characterization, and band structure calculation. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc., 2021, 57(1), pp. 305-17. doi: 10.1007/s41779-020-00533-6.
R. Alireza, A. Kamyar, M. Khakbiz and H. Basiri. Synthesis and characterization of strontium fluor-hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for dental applications. Microchem. J., 2020, 153(104485), pp. 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2019.104485.
C. Yanming, and X. Miao. Thermal and chemical stability of fluorohydroxyapatite ceramics with different fluorine contents. Biomaterials., 2005, 26(11), pp. 1205-1210. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.04.027.
M. Tahriri, M. Soulati-Hashjin and E. Hossein. Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite nanocrystals via chemical precipitation technique. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences., 2008, 4(2), pp. 127-134.
C. P. Dhanalakshmi, L. Vijayalakshmi, and V. Narayanan. Synthesis and characterization of fhap/chitosan nanocomposite and its biomedical application. Int. J. Nano & Matl. Sci., 2012, 1(2), pp. 81-96.
I. Nik?evi?, V. Jokanovi?, M. Mitri?, Z. Nedi?, D. Makovec, and D. Uskokovi?. Mechanochemical synthesis of nanostructured fluorapatite/fluorhydroxyapatite and carbonated fluorapatite/fluorhydroxyapatite. Journal of Solid State Chemistry., 2004, 177(7), pp. 2565-2574. doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2004.03.024.
C. Rey. Calcium Phosphates for Medical Applications. Calcium Phosphates in Biological and Industrial Systems, 1998, pp. 217–251. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-5517-9-10.
J. Ramyadevi, K. Jeyasubramanian, A. Marikani, G. Rajakumar, A. A. Rahuman. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of copper nanomaterials. Mater. Lett., 2012, 71, pp. 114-116. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2011.12.055.
V. N. Kuznetsov, L. B. Sukhodub, and L. F. Sukhodub. The study of the alginate/hydroxyapatite composites structural properties. Proceedings of the International Conference Nanomaterials: Applications and Properties., 2014, 3(2), 02NABM03, pp. 1-3.
Y. Luo, A. Lode, C. Wu, J. Chang, and M. Gelinsky. Alginate/nanohydroxyapatite scaffolds with designed core/shell structures fabricated by 3d plotting and in situ mineralization for bone tissue engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces., 2015, 7(12), pp. 6541–6549. doi: 10.1021/am508469h
A. Dubnika, D. Loca, and L. Berzina-Cimdina. Functionalized hydroxyapatite scaffolds coated with sodium alginate and chitosan for controlled drug delivery. Poly. Sci., 2016, 61,(3). pp. 193-199. doi: 10.3176/proc.2012.3.08
P. Nasker, A. Samanta, S. Rudra, A. Sinha, A. K Mukhopadhyay and M. Das. Effect of fluorine substitution on sintering behaviour, mechanical and bioactivity of hydroxyapatite. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 95 2019, 95, 136-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2019.03.032.
M. R. M. Roslan, N. L. M. Kamal, M. F. A. Khalid, N. F. M. Nasir, E. M. Cheng, C. Y. Beh, J. S. Tan and M. S. Mohamed. The state of starch/hydroxyapatite composite scaffold in bone tissue engineering with consideration for dielectric measurement as an alternative characterization technique. Materials., 2021, 14(8). 1960, pp. 1-17. doi: 10.3390/ma14081960.
H. Gul, M. Khan and A. S. Khan. Bioceramics: Types and clinical applications. In Handbook of Ionic Substituted Hydroxyapatites. Elsevier Publisher., 2020, pp. 53-83. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-08-102834-6.00003-3.
C. Rao, R. Wang, Y. Yang, F. Hatert, Q. Xia, X. Yue, W. Wang. Insights into post-magmatic metasomatism and li circulation in granitic systems from phosphate minerals of the nanping no. 31 pegmatite (SE China). Ore Geol. Rev., 2017, 91, pp. 864-76. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.08.017.
D. Kherifi, H. Belhouchet, S. Ramesh, K. Y. Sara Lee, A. Kenzour, S. Djoualah, M. K. G. Abbas, Y. H. Wong, S. Ramesh. Sintering behaviour of fluorapatite–silicate composites produced from natural fluorapatite and quartz. Ceram. Int., 2021, 47, pp. 16483-16490. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.02.216.
D. Thi Le, T. P. T. Le, H. T. Do, H. T. Vo, N. T. Pham, T. T. Nguyen, H. T. Cao, P. T. Nguyen, T. M. T. Dinh, H. V. Le and D. L. Tran. Fabrication of porous hydroxyapatite granules as an effective adsorbent for the removal of aqueous Pb (II) ions. J. Chem., 2019, 2019(8620181), pp. 1-10. doi: 10.1155/2019/8620181.
R. E. K. Billah, Y. Abdellaoui, Z. Anfar, G. Giácoman-Vallejos, M. Agunaou, A. Soufiane. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan/fluorapatite composites for the removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions and optimized parameters. Water Air Soil Pollut., 2020, 231(163), pp. 1-14. doi: 10.1007/s11270-020-04535-9.
A. Altaie, N. Bubb, P. Franklin, M. J. German, A, Marie, D. J. Wood. Development and characterisation of dental composites containing anisotropic fluorapatite bundles and rods. Dent. Mater., 2020, 8, pp. 1071-1085. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2020.05.003.
M. Okazaki, Comparison of hexagonal crystal structures between fluorapatite and polytetrafluoroethylene. Biomed. Mater. Eng., 2017, 28(1), pp. 3-8. doi: 10.3233/BME-171650.