Electrosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticle Using Green Tea Leaf Extract and Photocatalytic Methylene Blue Dye Degradation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/fwe.5.1.1121Keywords:
Electrosynthesis, silver nanoparticle, green tea leaf extract, photocatalytic degradation, methylene blue dyeAbstract
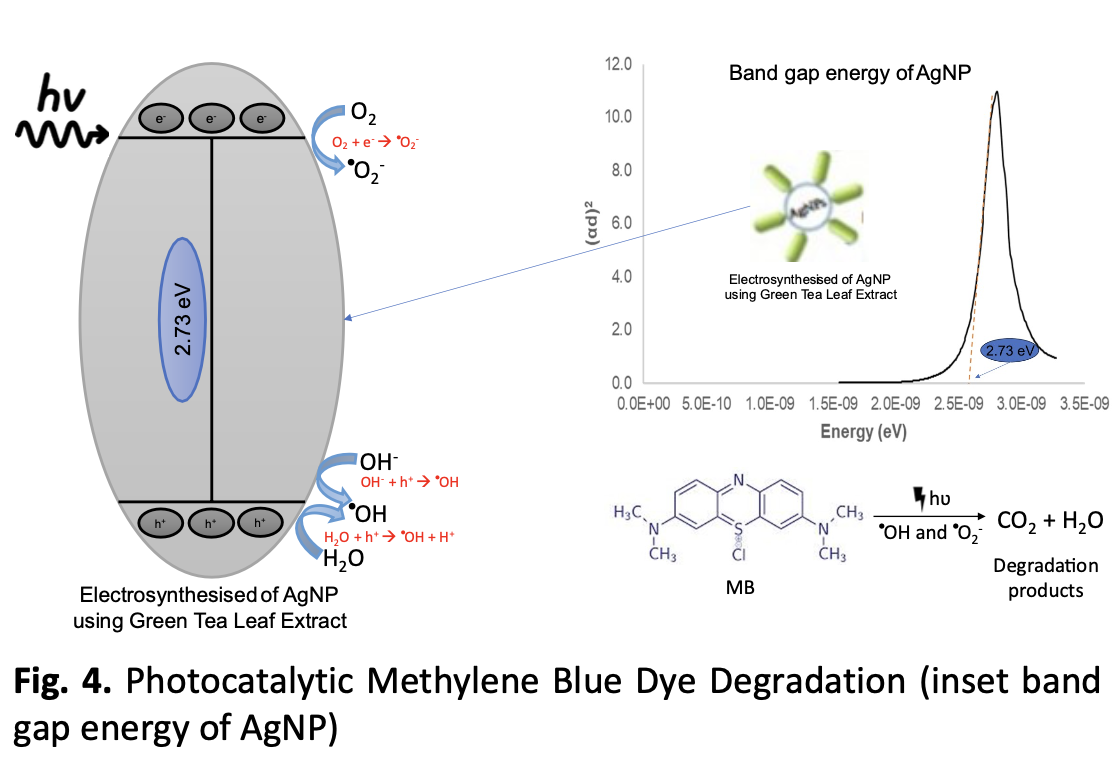
The high toxicity of synthetic dyes poses environmental and health risks, prompting the development of catalysts that improve degradation efficiency, particularly those that support sustainable wastewater treatment. AgNPs have extraordinary catalytic capabilities, making them effective at converting methylene blue (MB) dyes into less hazardous compounds. In this study, AgNPs were synthesised utilising tea leaf extract via electrolysis, providing a sustainable green chemistry strategy with excellent AgNP properties for degrading MB for a brief time. Using two pure silver electrodes and a green tea extract solution as an electrolyte, spherical AgNPs with a surface charge of -20 mV were produced. Tea extract biomolecules serve as bioreductors and capping agents, resulting in the formation of tiny, homogenous, and stable particles maintained until 15 weeks. The small size increases the surface-to-volume ratio along with electrical conductivity, which improves catalytic activity. HPLC analysis revealed that MB degradation reached 96.99% under sunlight for 72 min. Hence, this synthesis technique offers great opportunities for utilising AgNP-based nanocatalysis in wastewater treatment and environmental protection.