Investigation of Physicochemical Properties of Tabin Mud Volcano
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/fwe.6.1.4553Keywords:
Lapid volcano mud, physical characteristic, geochemical propertiesAbstract
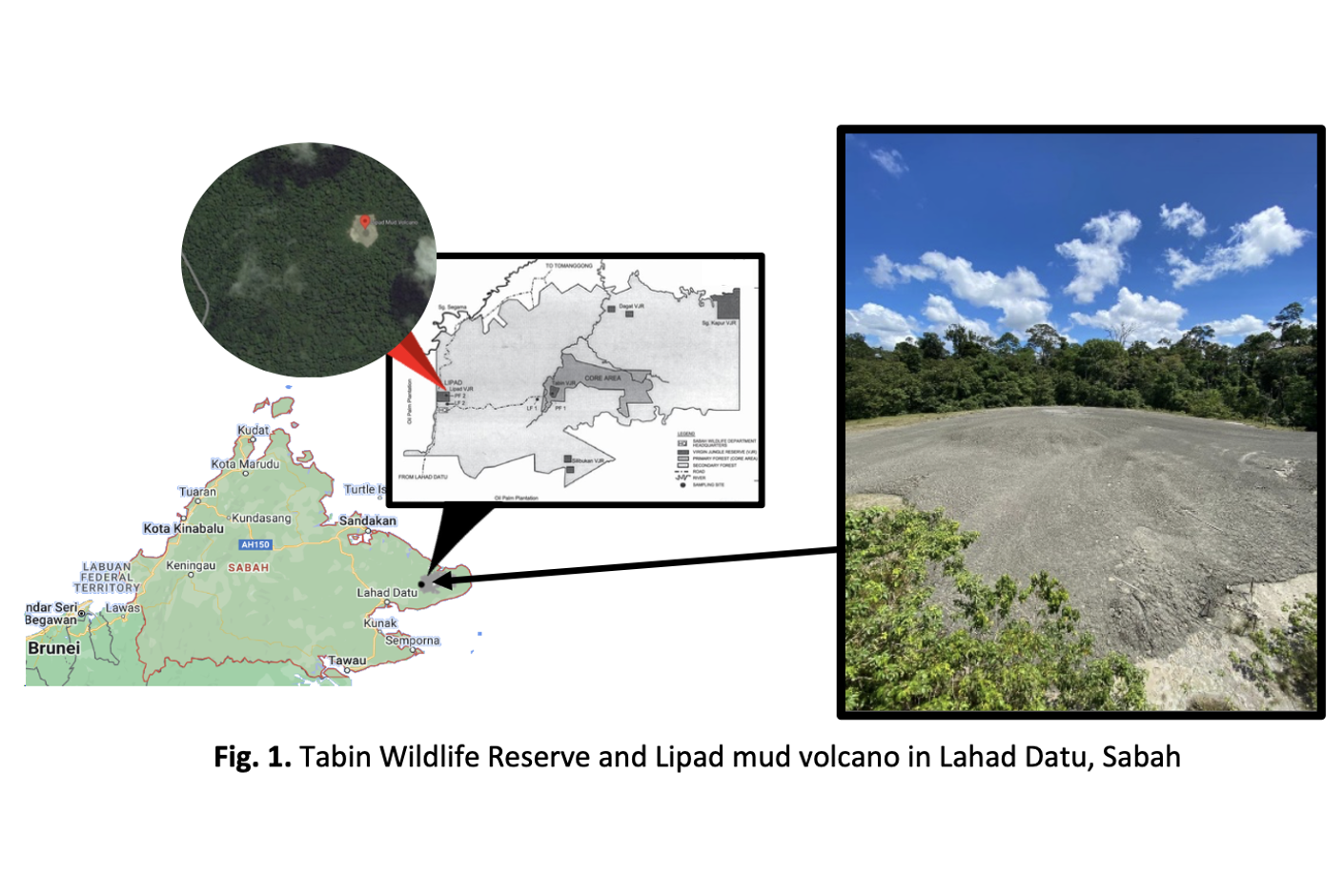
Volcano mud is a rare phenomenon found in specific areas, such as Lipad, Sabah, Malaysia, characterized by superficial vents that expel mud and gas flows. This process influences topography, soil properties, ecosystems, and landscapes. Understanding the chemical composition and physical properties of this mud is crucial for assessing rare-earth elements, fluid characteristics, and environmental impacts. In this study, the mud's physicochemical properties were analyzed, revealing a pH of 7, moisture content of 25.17%, and a particle size distribution of 6368 d.nm. Geochemical analysis via Energy Dispersive X-Ray (EDX) identified elements like Oxygen, Silica, Aluminum, Iron, and others, with O and Si being dominant. Rare clinochlore minerals were also detected using X-Ray Diffraction (XRD). The mud exhibited a negative surface charge of -26.5 mV and a unique morphology described as flakes and brittle, differing from typical soil structures as observed by Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM). Additionally, a high nitrogen compound content of 2.31% was detected, indicating potential gas release of nitrogen and carbon dioxide.