Impacts of Rainfall Variability on Water Quality Parameters in the Setiu River, Malaysia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/fwe.6.1.1331Keywords:
Rainfall impact, river management, Setiu river, seasonal variation, water qualityAbstract
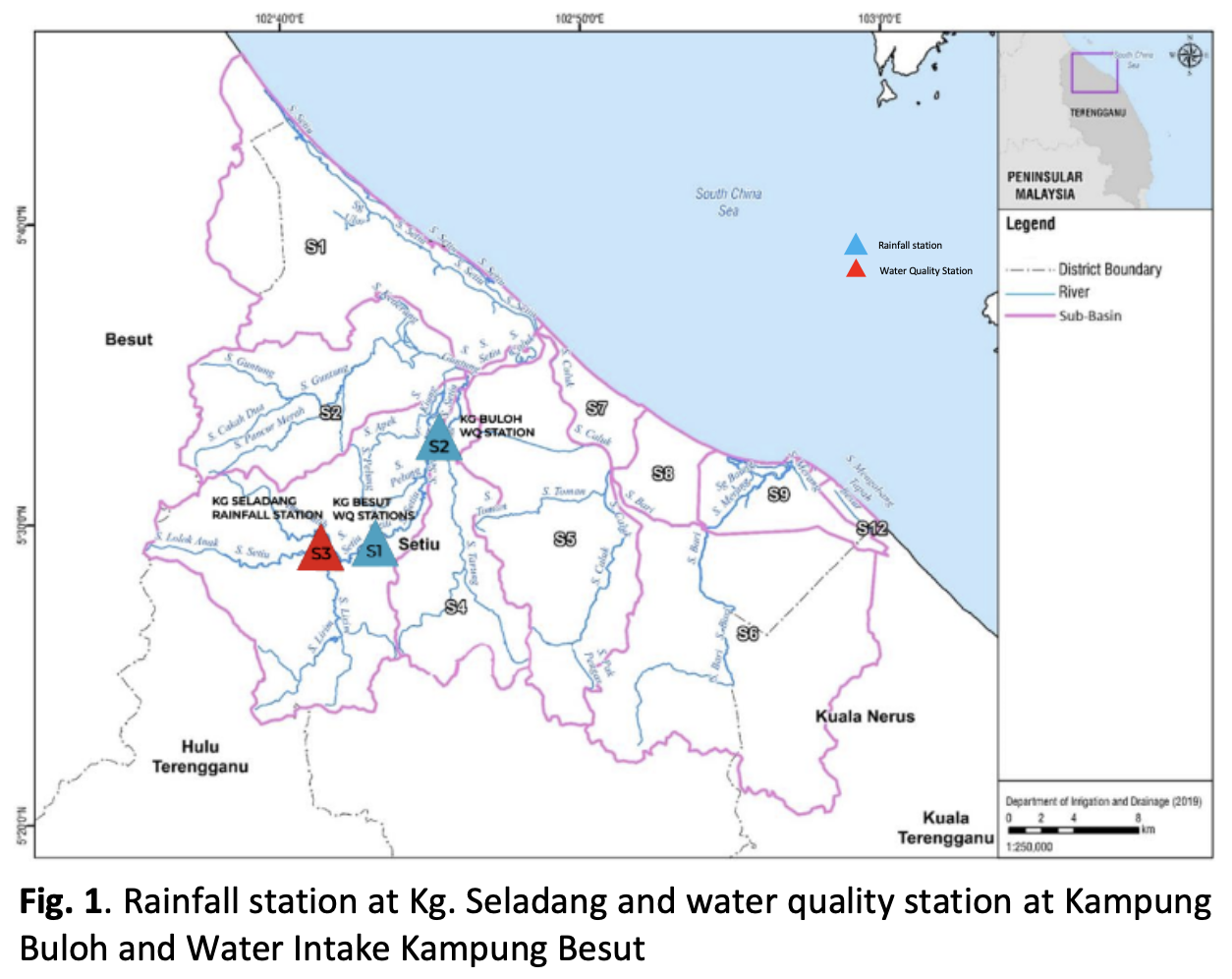
Water quality status serves as an essential indicator of the river’s health and its capacity for beneficial uses, reflecting changes in physical, chemical, and biological factors that are often sensitive to both natural and anthropogenic influences. The Setiu River in Terengganu faces an increasingly critical challenge in understanding the complex relationship between rainfall patterns and water quality dynamics. This study chooses the Setiu River as a case study and aims to address three primary objectives to gain insights into these dynamics: firstly, to examine the relationship between rainfall and water quality across wet and dry seasons; secondly, to analyze seasonal variations in specific water quality parameters in response to differing rainfall patterns; and thirdly, to investigate the relationship between water quality data at upstream and downstream monitoring stations. Rainfall data from the Department of Irrigation and Drainage (DID) and water quality parameter data from the Department of Environment (DOE) for Kampung Buloh and Water Intake Kg Besut stations were analyzed. The results reveal distinct seasonal differences, with correlation analyses showing a significant negative relationship between rainfall and pH during dry seasons, suggesting a dilution effect, and positive correlations between rainfall and NH3-N, indicating increased ammoniacal nitrogen levels. These findings imply that rainfall exerts substantial seasonal influence on key water quality parameters, with potential implications for ecosystem health, especially under prolonged dry or wet conditions. Nevertheless, a longer duration and more frequent data collection intervals are necessary to capture a comprehensive representation of rainfall’s overall effects on river water quality. Future studies should integrate discharge analysis with water quality parameters, which could provide a more detailed understanding of the interactions between rainfall, river flow, and pollution transport. This study contributes valuable knowledge to the broader discourse on river water management, emphasizing the importance of rainfall considerations in riverine health assessments.