Artificial Neural Network-driven Optimization of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles/PVDF Macrospheres in Fenton-like System for Methylene Blue Degradation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/armne.22.1.6884Keywords:
Artificial neural network, optimization, fenton-like, methylene blue dye, iron oxide nanoparticlesAbstract
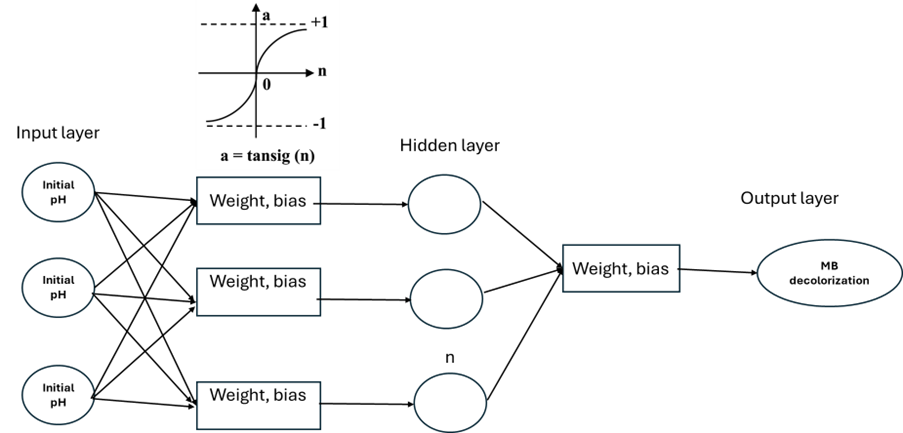
Efficient degradation of industrial dyes remains a critical challenge in environmental engineering. This study introduces a novel Fe3O4 nanoparticles/PVDF macrospheres in a Fenton-like system, optimized using an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) for the degradation of Methylene Blue (MB). A feedforward backpropagation neural network model to optimize and predict the performance of this advanced oxidation process under various operational conditions. The model was trained, validated, and tested with robust datasets, demonstrating high predictive accuracy and generalization capability. The Mean Square Error (MSE) and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) during testing were 0.0200 and 0.1414, respectively, indicating precise predictions. The coefficient of determination (R²) and correlation coefficient (R) were exceptionally high at 0.9744 and 0.9871, affirming the model's ability to capture the underlying dynamics of the degradation process effectively. The ANN-driven approach not only enhanced the efficiency of the MB degradation process but also provided significant insights into the scalability and applicability of the Fe3O4/PVDF system for practical water treatment solutions. This study underscores the potential of integrating advanced machine learning techniques with chemical engineering processes to achieve sustainable and efficient environmental management solutions, particularly for the treatment of recalcitrant wastewater contaminants.