Three-Dimensional Radiative Rotating MHD Nanofluid Flow of Over a Stretched Sheet with Homogeneous-Heterogeneous Chemical Reactions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/armne.21.1.112126Keywords:
MHD, rotating flow, nanofluid, stretching sheet, thermal radiation, heat sourceAbstract
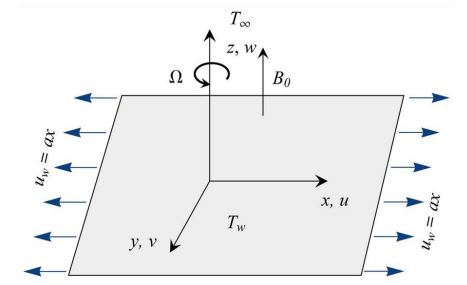
CNTs are employed in energy storage, device modelling, automobile parts, water filters, thin-film electronics, coating, and more. The continuous three-dimensional (3D) magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) rotational flow of water-based nanofluid comprising SWCNT and MWCNT past a stretching/shrinking sheet under magnetic field and homogeneous-heterogeneous chemical processes is examined in this study. Heat transport is also examined with thermal radiation and heat source/sink. The governing partial differential equations (PDEs) are transformed to non-linear ODEs using proper similarity transformations and solved numerically using MATLAB's bvp4c package. Graphs and tables show how magnetic field, rotational, suction/injection, thermal radiation, heat source/sink parameters, nanoparticle (NP) volume fraction, and homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions affect velocity, temperature, concentration, skin friction coefficient, and Nusselt number. For larger rotational parameters, the main velocity declines and the second velocity increases, and MWCNTs flow more than SWCNTs.