Structural and Optical Properties of Activated Carbon Derived from Eggshell
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/armne.21.1.104111Keywords:
Eggshell, activated carbon, phosphoric acid, structural properties, morphological propertiesAbstract
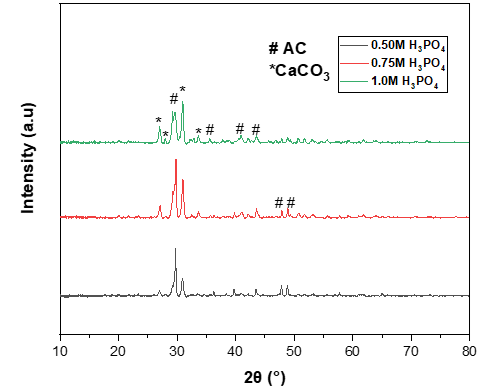
This research was done to prepare the eggshell as activated carbon (AC) using the simple chemical activation process. Phosphoric acid (H3PO4) at different molarities of 0.50, 0.75 and 1.00 M is used as an activation agent. All samples were analysed and characterized by using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). SEM images show irregular shapes of carbon. XRD patterns of AC were observed at 29.7°, 36.2°, 40.5°, 43.5°, 47.7° and 48.7° which corresponds to Braggs reflection planes of (201), (105), (107), (207), (206) and (304) respectively. The obtained diffraction peaks show the hexagonal crystal structure of carbon and are well matched with standard JCPDS: 721-616. SEM images show that the structure of AC are fake-like structures and exhibit partial geometrical shape when synthesized at 0.50 M. A broad and strong peak is observed at 1400 centimeter and a sharp peak appears at 872 centimeter due to stretching and bending vibration of the carbonate group present in the samples. The band observed at 1071 centimeter corresponds to the vibration of the phosphate group.