Design Considerations of Implantable MEMS Sensor for Bladder Pressure Monitoring: A Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/armne.21.1.89103Abstract
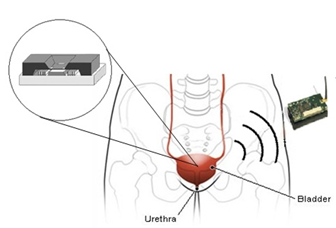
One of the main urinary disorders that impairs the bladder's capacity to regulate urine flow is urinary incontinence (UI). Currently, the new development of wireless implantable MEMS sensors has been studied to replace current clinical test of bladder pressure. This new invention grants a long-term pressure monitoring within the bladder, less painful with non-surgical, reducing the potential of infection thus maintains the patient’s quality of life. However, developing implanted BioMEMS sensors pose challenging tasks due to various constraint requirements that need to be fulfilled such as appropriate measurement ranges and bandwidth, suitable transduction mechanism, biocompatible materials, structural shape and size as well as wireless telemetry capability. This paper presents a review on implantable MEMS sensors and design challenges specifically for bladder pressure monitoring application.