Fabrication and Characterization of Nanocoils CNT/PLA Filament at Different Filler’s Percentages as Electromagnetic Wave Absorbers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/armne.19.1.8698Keywords:
EMI pollution, carbon nanocomposites, fillers, reflection loss, 3D printingAbstract
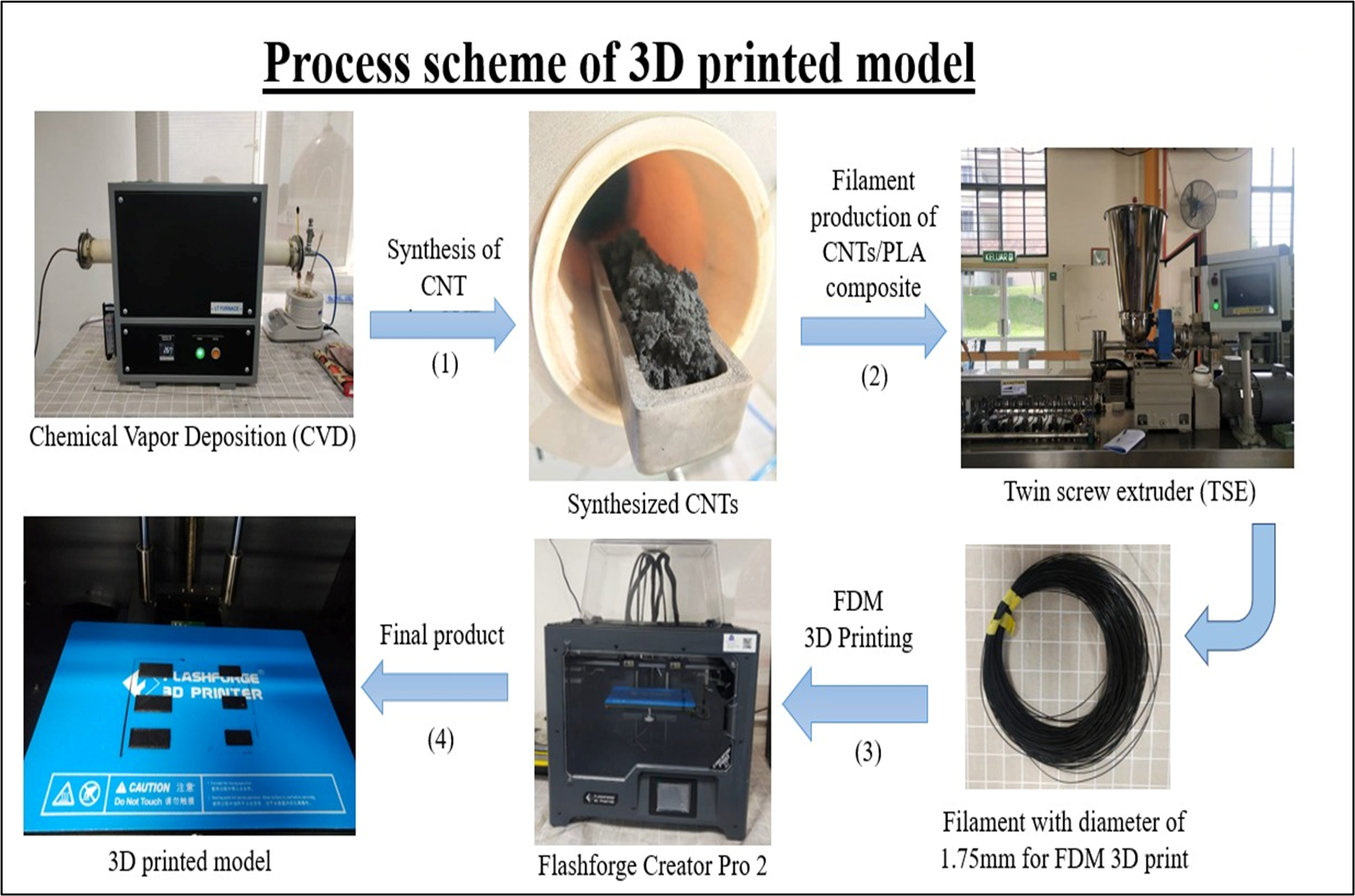
The rapid development of electronic technology and communication networks has resulted in high levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI) pollution, indirectly making electromagnetic wave (EMW) absorbers of great interest among researchers. The characteristics of an ideal EMW absorber should be lightweight, thin, strong and capable of absorbing the EMW in a broad frequency range. Recently, carbon-based materials such as carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have gained good popularity for their unique properties including lightweight, high mechanical strength, good electrical and thermal conductivity and wide frequency bandwidth. However, carbon nanotubes are very conductive and tend to agglomerate due to the van der Waals forces. Therefore, the incorporation of CNTs into polymer helps to improve the EMW absorption mechanism. This research focuses on fabricating electromagnetic wave absorbers with nanocomposite based on CNT/PLA filament for additive manufacturing (3D printing). Polylactic acid (PLA) with different weight percentages of CNT fillers (1, 3, 5 wt%) was extruded to fabricate a composite filament of a diameter of 1.75 mm. The results show that different percentages of CNTs fillers have a significant effect on the morphological and crystallographic phase structure, Raman scattering and EMW absorption properties.