CFD Based on The Visualisation of Aortic Valve Mechanism in Aortic Valve Stenosis for Risk Prediction at The Peak Velocity
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/armne.17.1.5668Keywords:
Aortic valve stenosis, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), Navier-Stokes equation, hemodynamic parametersAbstract
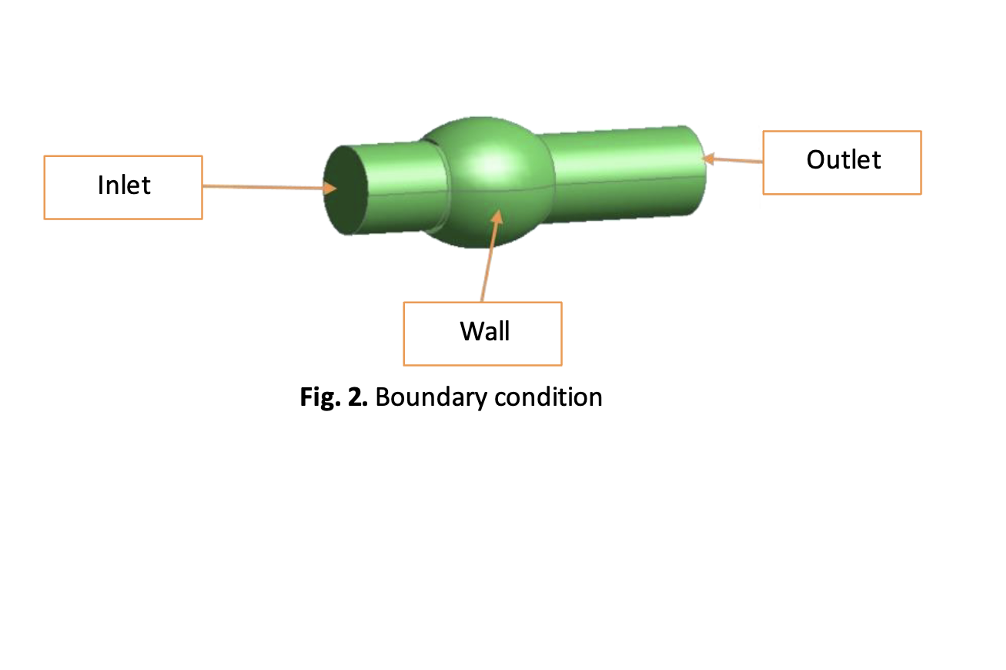
Aortic valve disease plays a crucial role in the development of cardiovascular disease (CVD), leading to increased rates of mortality and morbidity. Two diseases, aortic valve regurgitation and aortic valve stenosis are known to occur in the aortic valve. However, aortic valve stenosis is gaining attention due to its severe impact on the patient. The malfunction of the aortic valve might be affected by blood flow, which leads to stenosis. This study aims to investigate the blood flow re-circulation on the aortic valve in different stenotic regions when the blood’s velocity reaches the pick flow of the time in the systole phases. Four different models of aortic valve stenotic are designed using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The computational fluid dynamics (CFD) approach governed by the Navier-Stokes equation is imposed to identify the characteristics of the blood backflow at the left ventricle. Several hemodynamic factors are considered, such as time-averaged wall shear stress (TAWSS), oscillatory shear index (OSI) and relative residence time (RRT). The blood flow characteristic is expected to be chaotic, especially at the highest percentages of aortic valve stenosis, presenting the worst condition to the heart. This finding supports healthcare providers in foreseeing the deterioration of the patient’s condition and opting for aorta valve surgery replacement.