Formulation of Graphene Nanoplatelets Water-Based Nanofluids using Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as Surfactant
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/armne.16.1.3547Keywords:
Graphene nanoplatelets, polyvinylpyrrolidone, stability, thermal conductivity, viscosityAbstract
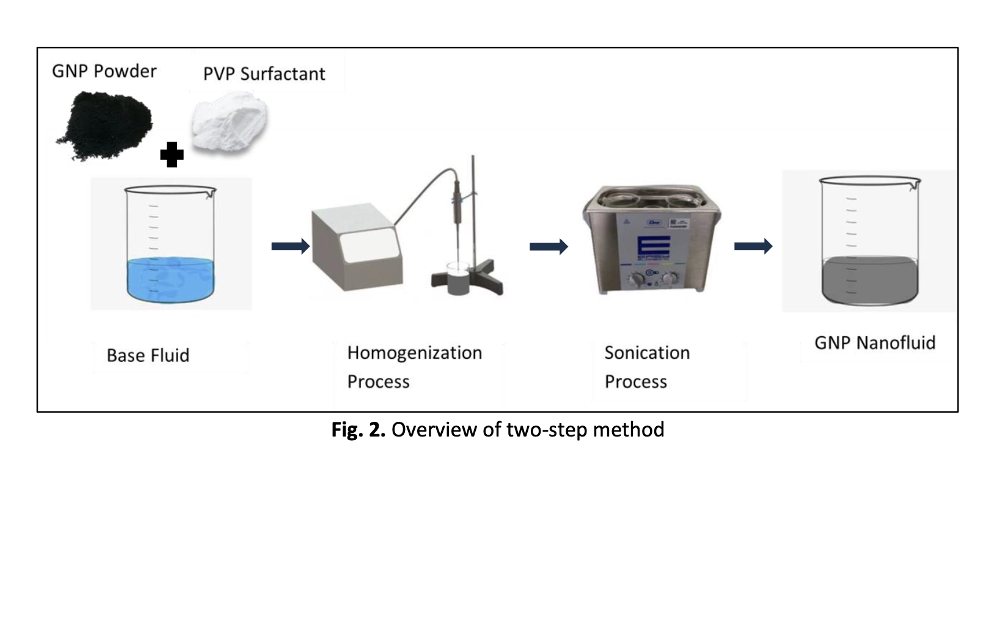
Graphene nanoplatelets (GNP) have garnered significant interest owing to their remarkable mechanical properties, making them ideal materials for enhancing the heat transfer properties of nanofluids. However, the agglomeration of GNP in water-based nanofluids remains a significant challenge, limiting their practical applications. In this study, a comprehensive investigation into the formulation of water-based nanofluids using GNP is presented, with a focus on the incorporation of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as a surfactant to enhance their stability and dispersion. The nanofluid formulations were systematically prepared with varying concentrations of GNP and PVP to optimize their thermal properties. Additionally, the thermal conductivity and viscosity of the nanofluids were examined over a range of temperatures and concentrations. The results show that the formulation of GNP with 0.6 wt.% shows great potential as a nanofluid with 0.6611 W/mK and 1.22 mPa.s for thermal conductivity and viscosity, respectively. The findings also demonstrate that the incorporation of PVP significantly improves the stability and dispersion of GNP in water, leading to enhanced thermal conductivity and manageable viscosity. These findings contribute to the application of this nanofluid in various industries, specifically solar energy.