Mixed Convection Hybrid Nanofluid Flow past a Stagnation-Point Region with Variable Viscosity and Second-Order Slip
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/armne.12.1.121Keywords:
Hybrid nanofluid, mixed convection, second-order velocity slip, variable viscosity, dual solutions, stability analysisAbstract
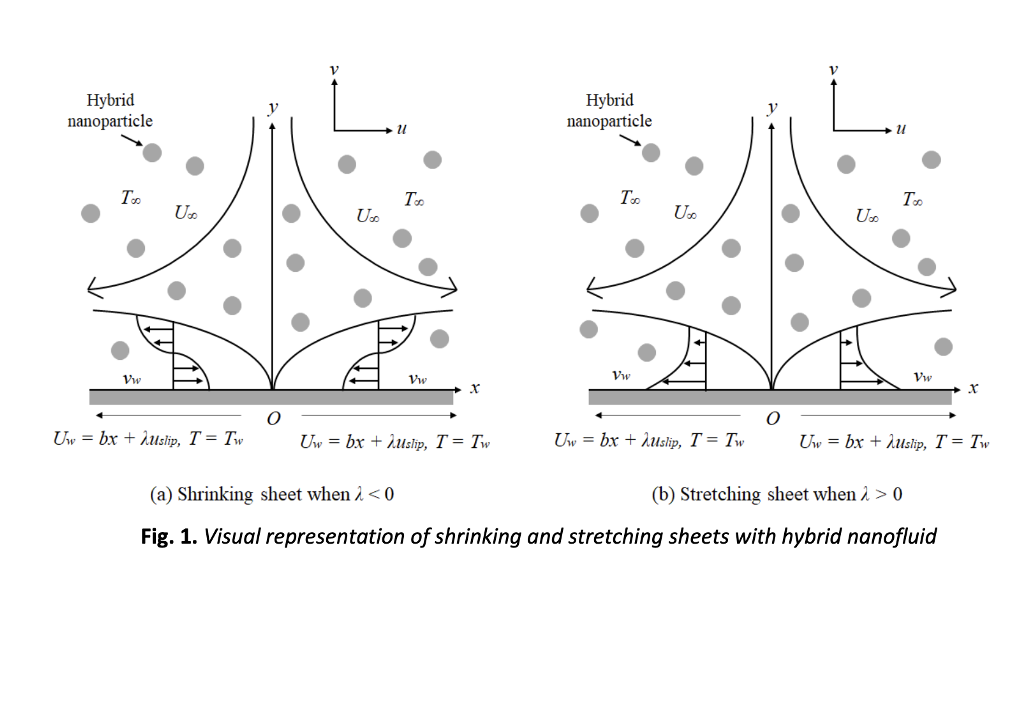
The objective of this study is to investigate the effects of mixed convection flow dispersed with a hybrid nanofluid over a permeable shrinking surface past a stagnation-point region considering the influence of second-order velocity slip and variable viscosity on the flow behaviour. For the hybrid nanofluid, water (H2O) is chosen to be the base fluid, while silver (Ag) decorated copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles are employed as the hybrid component. To achieve the mathematical model, a suitable method of similarity transformation is applied to convert the partial differential equations (PDEs) model into a system of non-linear ordinary differential equations (ODEs). The shooting technique method and bvp4c solver in MAPLE and MATLAB are employed to obtain the analytical solutions of the mathematical model. The obtained results, including the impacts of variable viscosity, second-order velocity slip, mixed convection parameter, suction, shrinking parameter, and nanofluid volume fraction, are presented through tables and figures. The study reveals the existence of dual solutions (upper and lower branches) prior to shrinking sheet . Furthermore, the thermal distribution exhibits mixed behaviours with respect to the variable viscosity number and second-order slip parameter, while demonstrating an increase with the presence of Ag- . The velocity distribution experiences an enhancement with both concentration and variable viscosity number. Stability analysis is then employed and shows that the first branch is stable, whereas the second branch exhibits an opposite outcome.