Simulation Study on the Heat Performance of Different Nanofluids for Rotating Detonation Engine Cooling
Keywords:
Nanofluids, RDE cooling system, Heat transfer, visible aidsAbstract
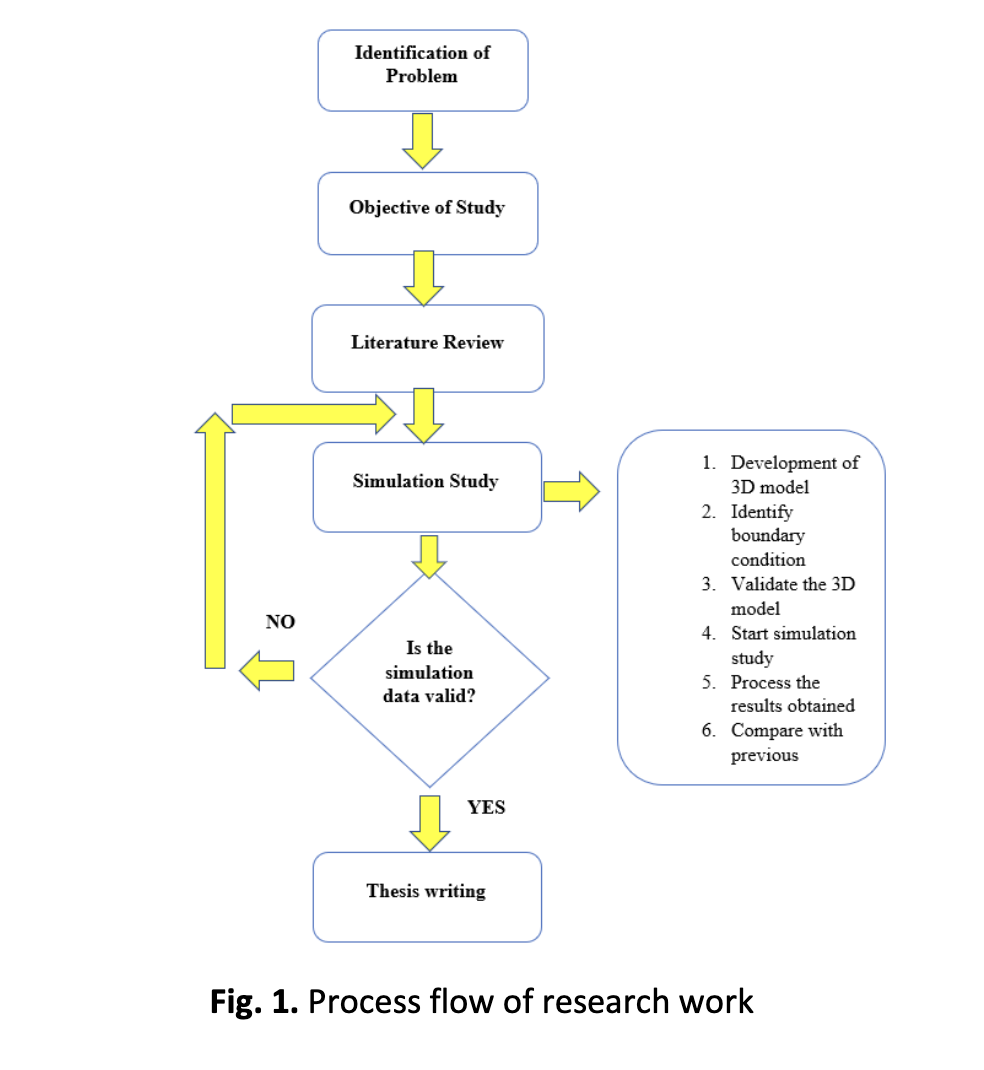
The objective of this numerical study is to analyze the heat transfer performance of different nanofluids for RDE cooling. Based in previous researches, they used water as coolants for their RDE cooling setup but in this research study, instead of using water, nanofluids were used numerically to see whether nanofluids can remove heat better than water, which directly contributes to improvement of RDE cooling system. The nanofluids consists of titanium dioxide, copper oxide and aluminium trioxide nanofluids which were labelled as Nanofluid 1, Nanofluid 2, and Nanofluid 3. The boundary conditions include varying the mass flow rate of 0.0034 kg/s, 0.0102 kg/s and 0.0170 kg/s, with the detonation temperature set to 573K and inlet temperature of 300K and mild steel as the solid part of the model. Based on the simulation result obtained, it shows that Nanofluid 2 possess the best heat transfer performance, which around 26% increase of rate of heat transferred compared to Nanofluid 3 and around 40% increase compared to Nanofluid 1, at mass flow rate of 0.0034 kg/s.