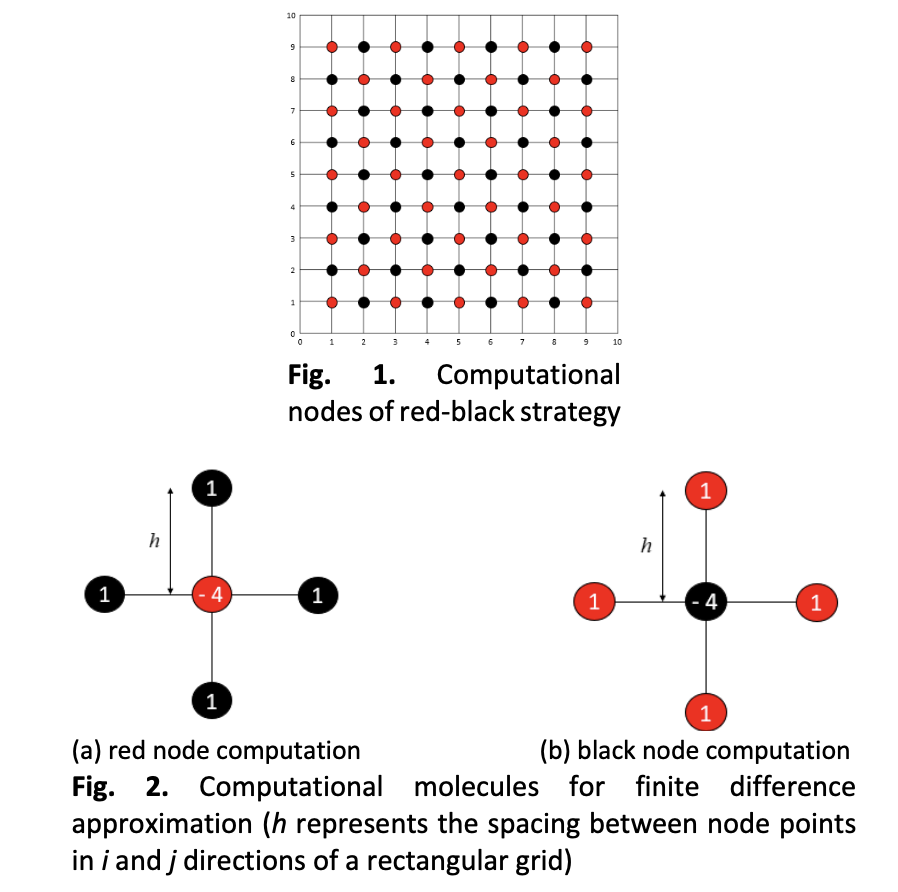
Path Navigation in Designated Environment using Modified TOR
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arca.38.1.3950Keywords:
Laplace's equation, Finite Difference Method, Over-Relaxation Iterative Techniques, path planning, obstacle avoidanceAbstract
Research in the field of path navigation efficiency has continuously progressed, particularly focusing on generating collision-free paths for agents moving within specific environments. Therefore, this study aims to tackle the path navigation problem using a numerical iterative approach. An improvise approach namely Modified Two-Parameter Over-Relaxation (MTOR) is introduced to address navigation challenges effectively. In numerical simulations, MTOR is utilized to derive solutions to Laplace's equation, known as harmonic functions. These harmonic functions are then used in a gradient descent scheme to generate smooth and collision-free paths for agents moving through the designated environment. The formulation of the MTOR iterative method is explained in detail, and multiple numerical experiments and simulations are carried out to assess its efficiency. The findings indicate that the proposed improvise method outperforms existing methods.
Downloads