Theoretical Analysis of Two-Phase Mixed Convection Flow: Effects of Fluid-particle Interaction and Mass Concentration on Velocity, Temperature and Skin Friction
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arca.38.1.2338Keywords:
Theoretical analysis, two-phase flow, fluid-particle interaction, mass concentration, mixed convectionAbstract
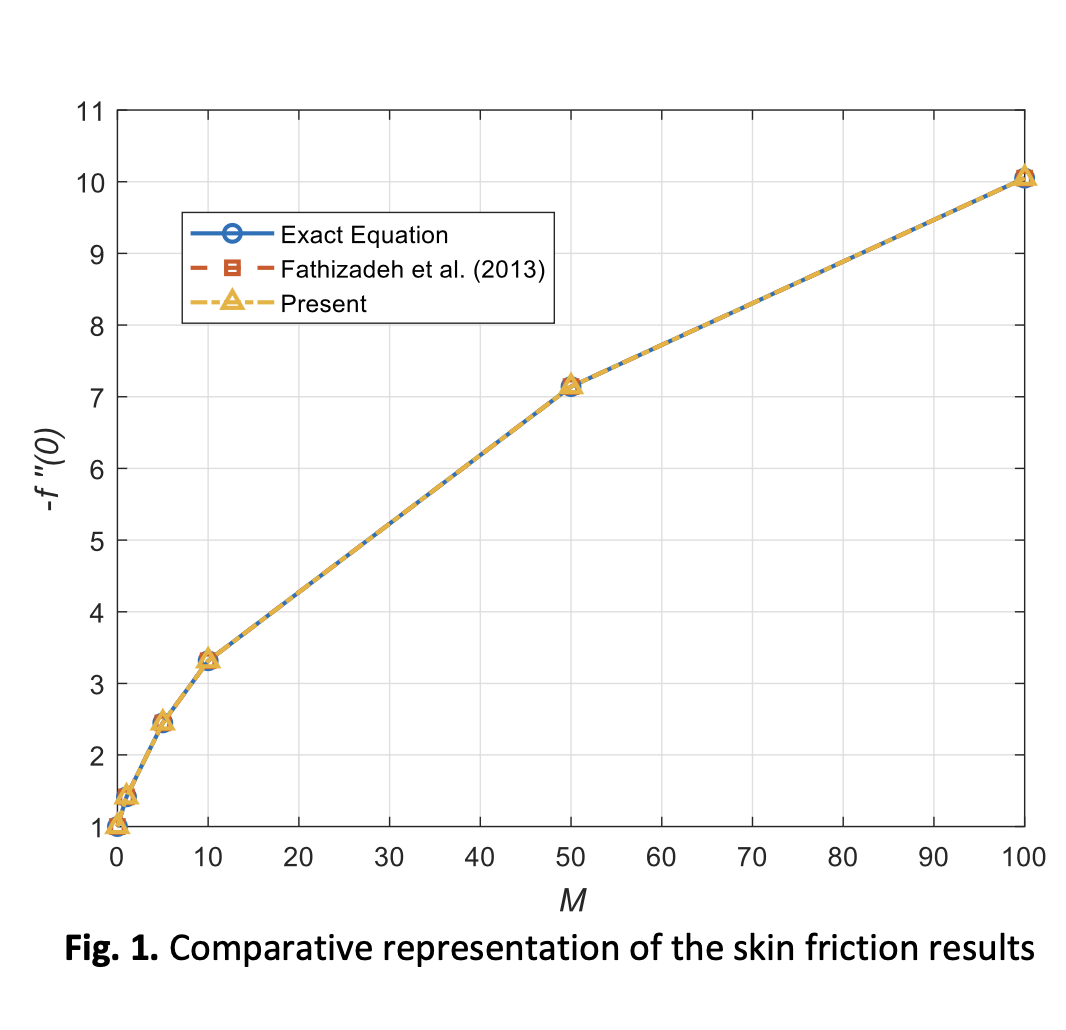
Research on Newtonian fluids, a fundamental area in fluid flow studies, serves as a key reference for more complex models. The deformation of fluid structure due to the presence of solid particles in Newtonian fluids necessitates a detailed analysis. Conventional models are insufficient to describe such systems, as they are categorized as two-phase fluid flows. The study of two-phase systems (fluid and solid) has gained significant attention due to its wide applications in real-life scenarios, including air and water pollution, blood flow in arteries, and coolant flow in vehicle engines. This field's high potential has driven researchers to find effective solutions to these challenges. The two-phase model not only focuses on fluid flow but also accounts for the interaction between the fluid and solid particles. This study theoretically examines a modified model that considers fluid phase and dusty phase under mixed convection case. Using an appropriate similarity transformation, the governing partial differential equations are converted into ordinary differential equations. The Runge-Kutta-Fehlberg method, implemented in the Maple software, is used to solve the obtained equations numerically. The study explores various physical parameters, including mixed convection parameter, fluid-particle interaction parameter and mass concentration parameter for both phases. The findings reveal that the presence of dust particles significantly affects the velocity and temperature behavior of both phases. Specifically, increasing particle concentration leads to a reduction in fluid velocity and temperature distribution.
Downloads