A Comparative Performance Analysis of Several Machine Learning Classifiers on the Credit Card Data
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arca.37.1.5064Keywords:
Credit card, fraud, classification, mahalanobis distance, accuracy, efficiencyAbstract
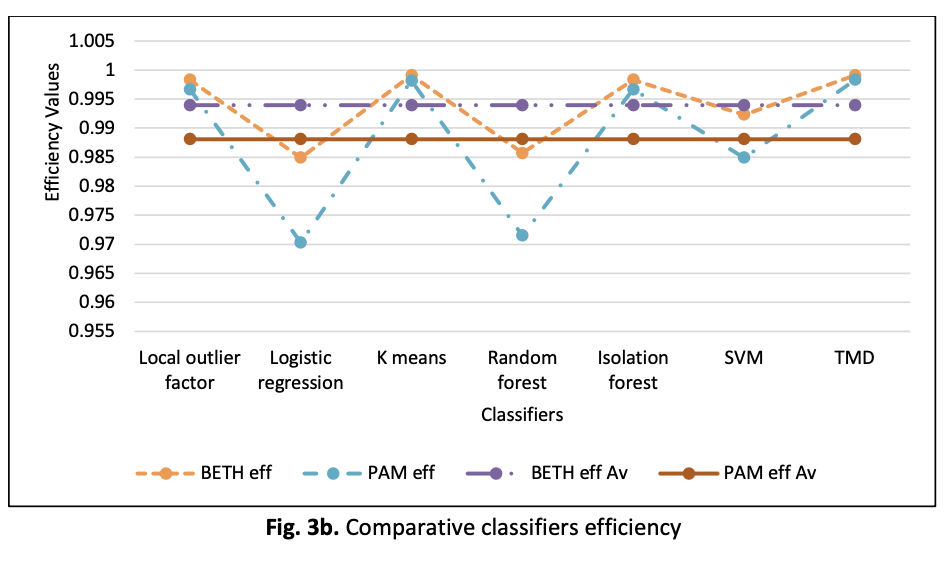
As customers tendencies learn rapidly about online transactions due to the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic, fraudulent transactions that mimic legitimate transactions will continue to increase unabated. Over the years, fraudulent transactions have been committed but the supervised and unsupervised machine learning classifiers and fraud detection techniques could not stop the fraud from occurring at the onset. However, fraudulent cases are detected after post-occurrence thereby recognizing these techniques as non-smart detection models because fraud could only be detected using past data sets. Various fraud detection or classifier techniques using machine learning techniques such as decision trees, random forests, k-means, and neural networks have been studied. Also, the possibility of overfitting due to the branch growth associated with the decision trees is a classifier performance problem. The application of the probability axiomatic metric (PAM) to determine the accuracy of the models is a classification evaluation problem because of the relatively moderate error rate. To overcome the above shortfalls, we proposed a threshold Mahalanobis distance (TMD) classifier and adopted BETH as a performance evaluation metric. The result revealed that TMD is comparable to neural network (NN), k-means, isolation forest, XGBoost, and random forest based on the credit card data set. The analysis showed that TMD and NN have higher efficiency compared to other classifiers. This study demonstrated that the TMD classifier is unique and could be applied to extract legitimate and illegitimate transactions from customer transaction data sets. The study concludes that TMD is robust and comparable to NN and the classification errors associated with BETH are minimal compared to PAM for both TMD and NN.
Downloads