Meta Analysis of Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) for Growth and Yield Related Traits under Drought Stress in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
Meta Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arca.37.1.120Keywords:
Meta analysis, yield, growth, wheat, droughtAbstract
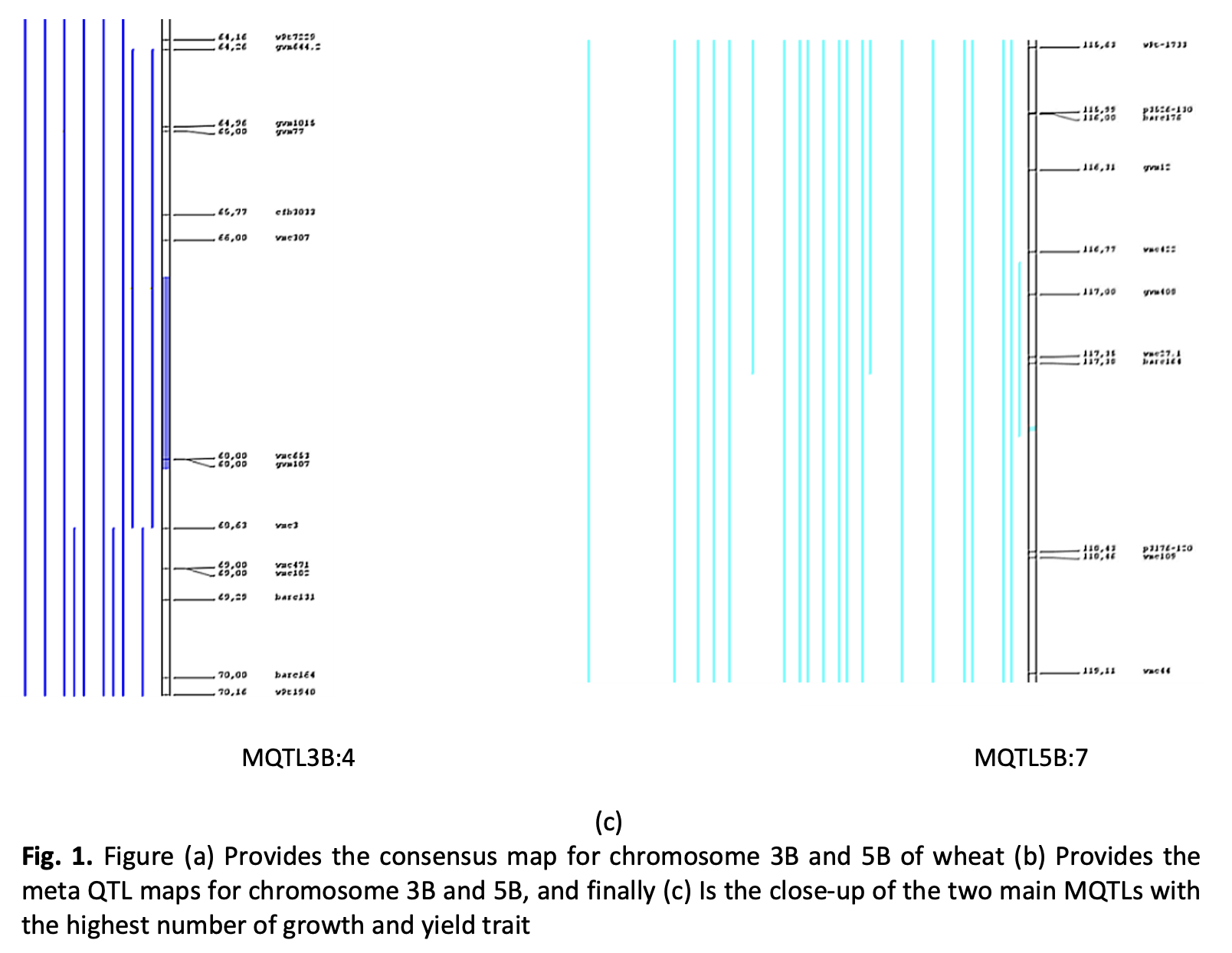
Wheat is a critical crop in temperate climate zones, with demand rising in both urbanized and industrialized countries. However, drought stress significantly impacts global wheat yield, highlighting the need for breeding programs focused on drought tolerant wheat. This study conducted a QTL meta analysis to identify growth characteristics and yield related traits associated with drought tolerance in wheat. Stable QTLs were targeted across different varieties and experimental environments to ensure the success of these breeding programs. The study compiled drought tolerant QTLs from 27 previous studies, identifying a total of 951 QTLs, which were used to create a consensus map. Of these, 538 QTLs were related to yield characteristics, while 413 were linked to growth characteristics associated with drought tolerance. BioMercator V4.2.3 software was employed to generate consensus maps and perform the meta analysis. The consensus map, derived from the combined data, consisted of 457 QTLs spanning a total genetic map length of 727,819 cM. The meta analysis identified 140 MQTLs, with MQTL 5B:7 and 3B:4 emerging as the most significant, harboring 24 and 20 QTLs, respectively. These chromosomes contain major QTLs associated with drought tolerance. The findings provide valuable insights that can be utilized in breeding programs to enhance drought tolerance, yield, and growth in wheat.
Downloads