Deep-Learning Pre-Processing for Improvement of K- Means Cluster Analysis of Seniors’ Walkability in Hradec Kralove And Ostrava (Two Middle-Sized Czech Cities)
Keywords:
Cluster analysis, walkability, elderly, deep learning, k-means, HDBscan, N2DAbstract
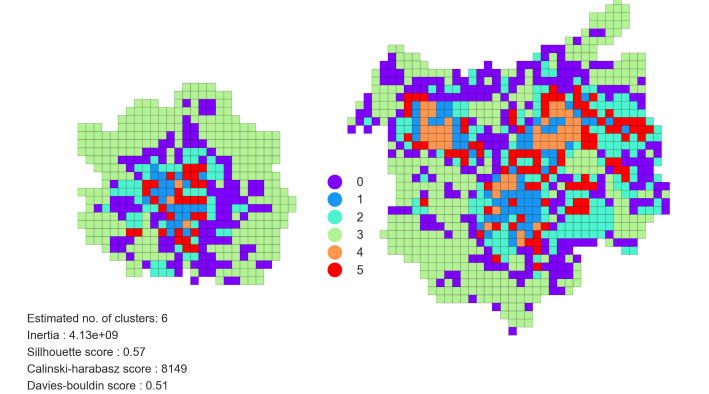
Increasing people's well-being, reducing traffic, and creating a healthy urban environment in contemporary cities is quite dependent on excellent conditions for walking and generally for supporting human physical activity. Various indicators and metrics exist to assess walking conditions. One of them is the walking index (WAI), representing indicators based on the environment. Walkability receives growing interest for vulnerable group of people, namely higher age elderly. Due to erosion of physical and financial capabilities, walking is considered as a safe and saving form of physical exercise to maintain health status, a platform for positive direct and indirect effects – improvement of quality of life (QoL), health status, well-being; decreasing of traffic and related pollution; direct economic effect (quotations). Our motivation was to improve classic cluster analysis of urban walking conditions for the elderly to obtain more specific and robust classification, assess the potential of advanced machine-learning based clustering methods to discover more specific classes of urban conditions to better address improvement of urban conditions using specific urban planning measures. And because classic K-means does not provide satisfactory results, we focused also on HDBScan, Soft Clustering and N2D method. Finally, the results proved the N2D method is the efficient method of clustering and provides improved results for urban walkability characteristics.
Downloads