Measures of Effectiveness for E-learning of University Students during the Covid-19 Pandemic Using the Statistical Model
Keywords:
E-learning, Effectiveness, Covid-19, PandemicAbstract
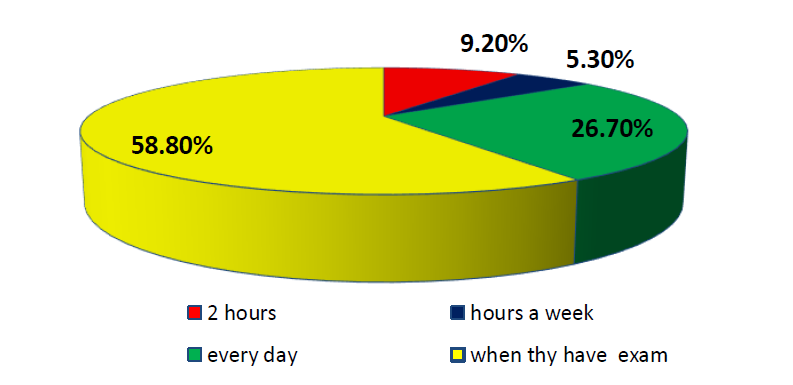
E-learning was considered the best solution for continuing education during the COVID-19 pandemic, especially in tertiary education. The present study aims to analyse the effectiveness of E-learning for the students at university level during the Covid-19 outbreak. Data have been collected through questionnaire and were given to 500 students, with a return rate of 96.9% among respondents who use module and classroom tools, techniques, or platforms. The statistical model was applied to the analysis of the questionnaire. Principle component analysis techniques were used to determine the nine variables' efficacy on the E-learning model, and Cronbach’s alpha test was used to measure the reliability and internal consistency of the associated components. The outcome of the study supports the assumption that E-learning entails Familiarity with the technology; Usability, Learned skills, and Competency; Quick Responsiveness; Learning Quality of the learner; Time and Cost; Faster Learning; Information quality; and Knowledge sharing.
Downloads