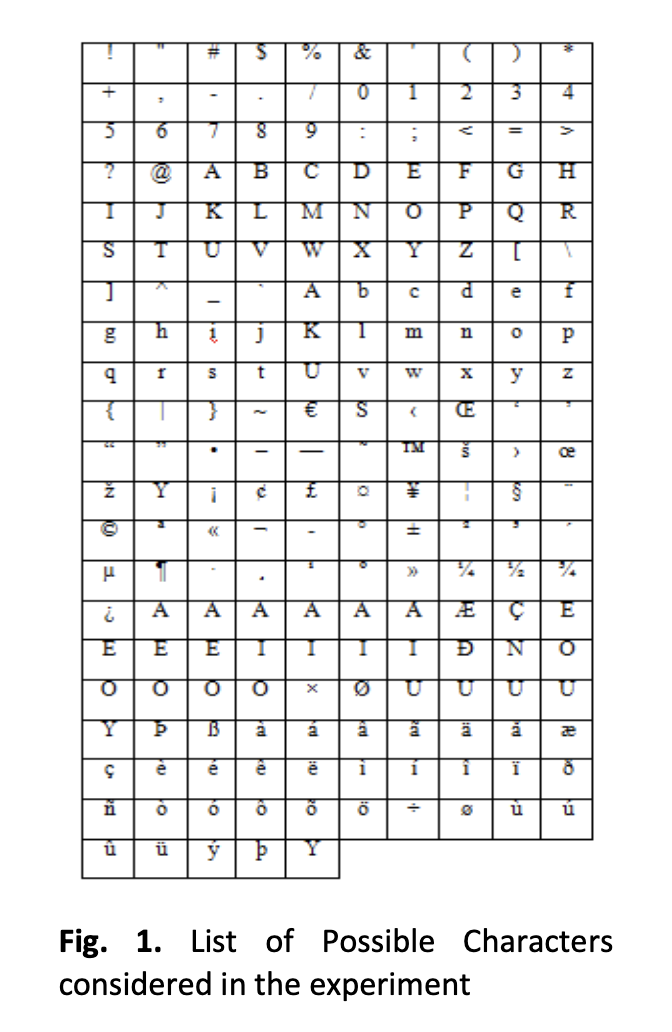
Performance Analysis of Three Classical Encryption Algorithms, Simple Substitution, Caeser, and Periodic Permutation (the Three SCP) in Encrypting Database Transactions
Keywords:
Database security, database transaction, database transaction security, classical encryptionAbstract
Encryption was introduced and implemented in many Database Management Systems (DBMSs) as one of the solutions for securing databases. However, Securing database transactions and data they hold while they are existing in memory or even during their transmission throuh computer networks media should be also given big attention. The core objective of this paper is that to measure the performance of the three classical encryption algorithms: Simple Substitution, Caesar cipher, and Periodic Permutation respectively for encrypting such database transactions and text data they hold which is sort of encrypting data-at-rest. Performances are measured herein in terms of time, memory usage and CPU efforts. The expirement was performed to many categories of transactions, those categories are categorized according to two issues: the size of data that the transactions hold, and the type of transactions itself. This experiment can be a base to enable Database Designers to design algorithms that has the ability to decide which one is the optimal according to type of database transaction waiting for processing as well as size of data that it consists of, and also other computing processing components such as CPUstate and RAM consumption ratios.
Downloads