Organizational Commitment and Organizational Citizenship Behaviour: The Moderating Effect of Trust among Fast Food Restaurant Employees
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arbms.37.1.2338Keywords:
Organizational citizenship behavior, organizational commitment, organizational trust, moderator, fast food restaurantsAbstract
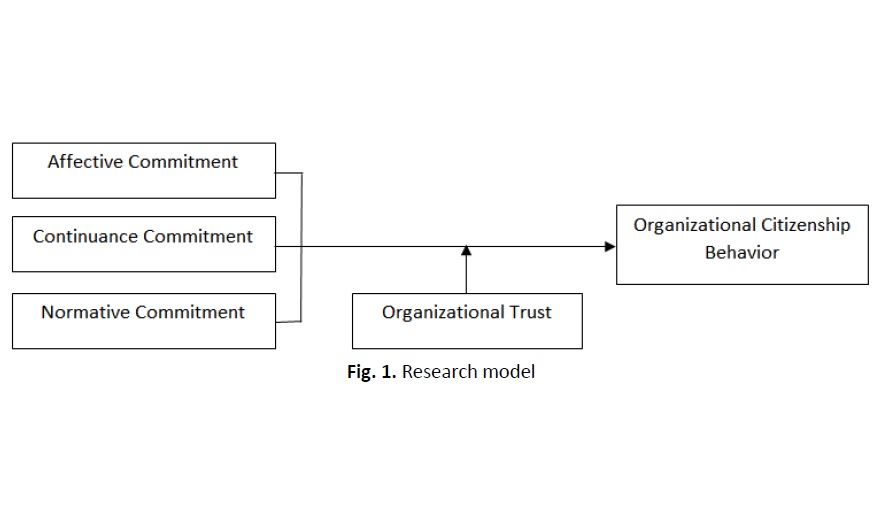
There is an increasing employee turnover rate in the fast-food service industry. When organizational citizenship behavior among the employees is low, they tend to be demotivated, and their productivity will be reduced, affecting the tasks or jobs their supervisor assigns. Organizational citizenship behavior refers to the voluntary behavior exhibited by the employees while in the organization. Employees with this behavior tend to work harder as it boosts their motivation and induces passion. The study investigates the effect of organizational commitment on organizational citizenship behavior among the employees in fast-food restaurants in Negeri Sembilan. There are three-dimensional components of organizational commitment, namely: (1) affective commitment, (2) continuance commitment, and (3) normative commitment. Furthermore, this study also examines the role of organizational trust as a moderator of the relationship between organizational commitment and organizational citizenship behavior. This study was conducted covering various levels of employee positions in fast-food restaurants. This study's respondents are from the fast-food restaurant workers at KFC, McDonald's, Pizza Hut, Subway, and Domino in Negeri Sembilan. The study used disproportionate stratified random sampling that resulted in 181 employees, and the data was collected using a questionnaire survey. This research data has been analysed through descriptive statistics and hierarchical regression analysis. The results found affective, continuance, and normative commitment associated with organizational citizenship behavior. In addition, trust has also contributed to significant factors that have influenced the level of organizational citizenship behavior among employees. The trust moderates the relationship between affective commitment and organizational citizenship behavior. However, trust does not moderate the relationship between continuance and normative commitment, and organizational citizenship behavior.