A Review of Flood Resilience Implementation in Malaysia
Keywords:
Flood resilience, CMMI, disaster risk reduction, Malaysia, natural flood managementAbstract
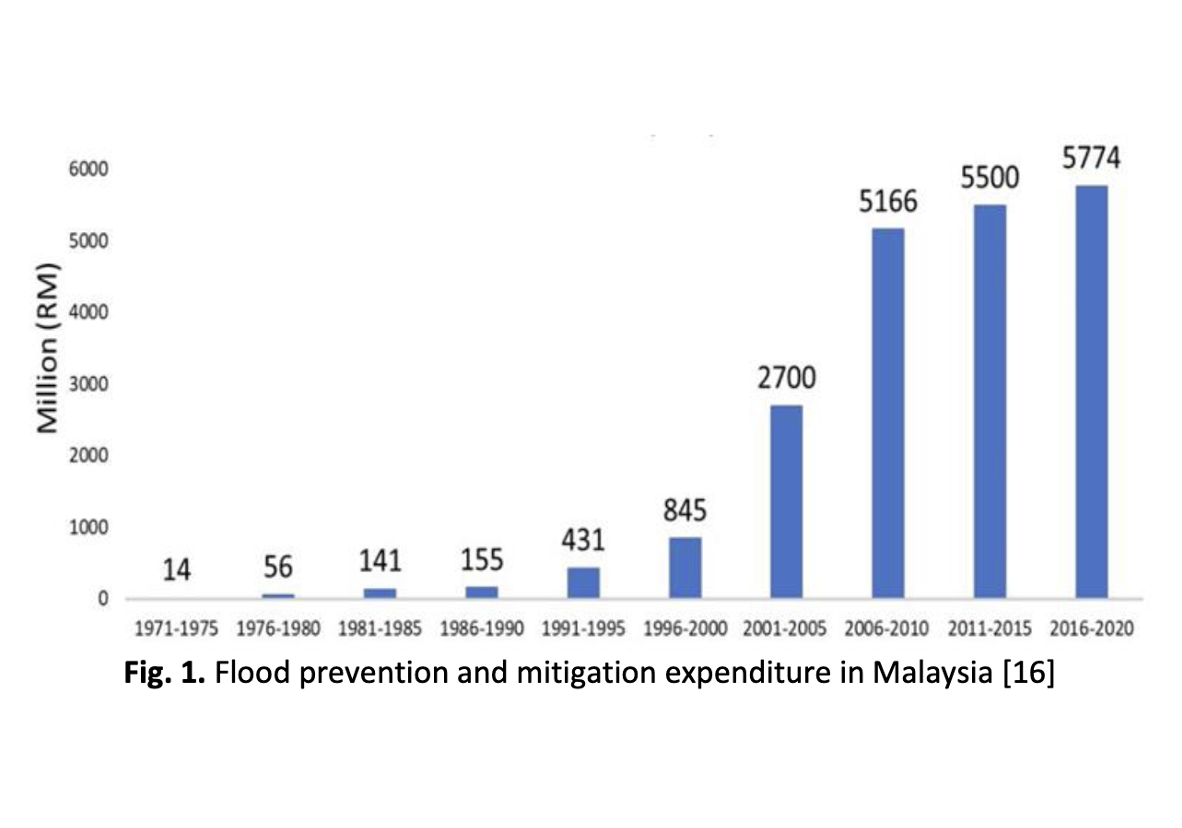
Floods are Malaysia’s severest catastrophe that can result in the loss of life and property. They also have devastating consequences and effects to the economy, people and environment. Malaysia records an average annual damage of around RM 36 billion as reported in the previous study and this is expected to increase in the near future. Investments in flood prevention and mitigation have been rising, from around RM14 million (1971) to RM5.774 billion (2020). This research aims to understand the current scenario of flood resilience implementation in Malaysia in strengthening governance. From the study, CMMI is identified as a suitable tool to assess flood resilience maturity in Malaysia. Flood resilience in Malaysia that can potentially lead to a reduction in flood risk is benchmarked against good standard practice led by the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction (SFDRR) 2015-2030. Recognizing the complexity of hazards and their impacts, while Malaysia is using this SFDRR framework, there is still concern about the severity of loss and management of flood risk. Successful implementation of flood resilience is accomplished when the four stages of disaster risk reduction (DRR) consisting of flood prevention/mitigation, preparedness, response and recovery are effectively prioritised in the short, medium and long-term plans to prevent new risks, reduce existing risks, and strengthen societal and environmental resilience. Pursuant to the anticipated outcome and goal, there is a need for focused actions within and across sectors by states at local and national levels starting from understanding flood risk, strengthening flood risk governance, investing in disaster risk reduction for flood resilience and enhancing flood emergency preparedness for successful response and recovery. The findings will be of interest to policy and decision makers in enhancing their understanding of the current scenario of flood resilience in Malaysia, the improvements to be made and investments to be spent on approximately 10 percent of the total area of Malaysia, which have been identified as flood-affected areas.