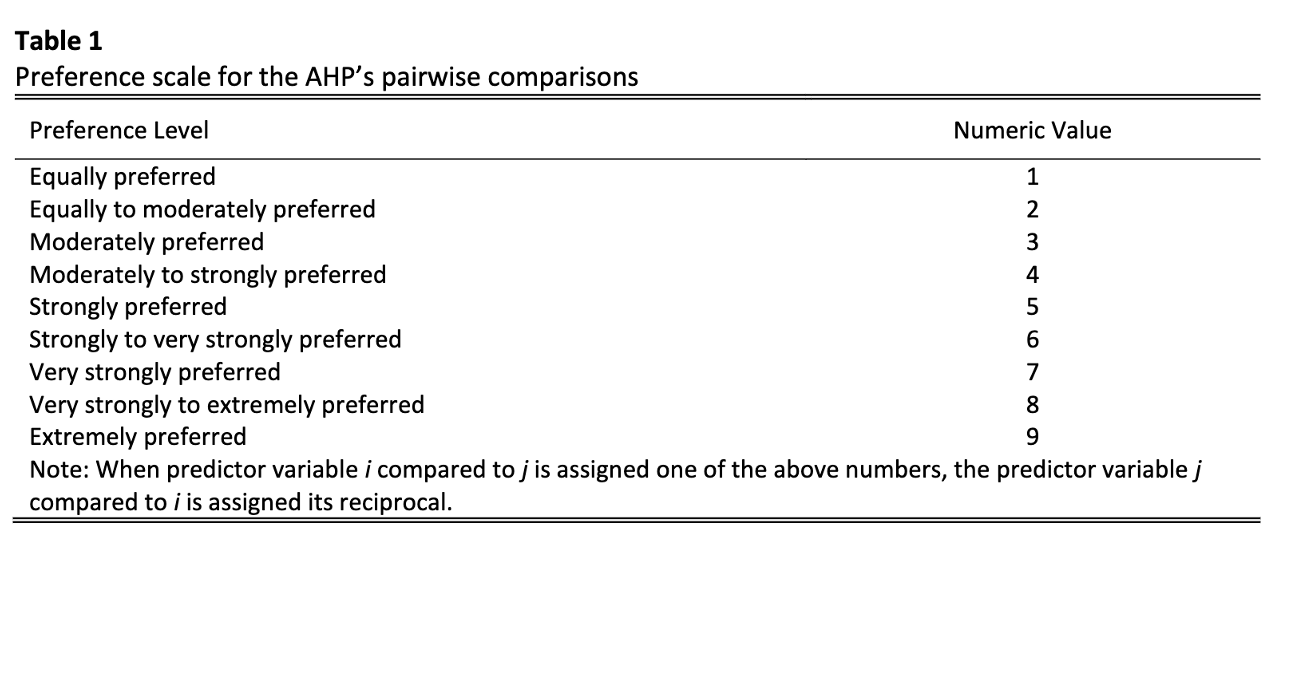
Identifying Relevant Predictor Variables for a Credit Scoring Model using Compromised-Analytic Hierarchy Process (Compromised-AHP)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arbms.20.1.113Keywords:
predictor variables, loan defaulters, compromised-AHP, credit scoring modelAbstract
Developing an efficient credit scoring model to reduce the risk of personal-loan defaulters involves the selection of manageable reliable predictor variables in order to avoid the potential clients from providing too much information and to reduce the burden of a bank from keeping huge historical data, which can be burdensome and costly. The objective of this paper is therefore to illustrate how compromised-AHP can be used as one the methods to select such relevant reliable predictor variables before the final credit scoring model is constructed. A case study involving four experts from a bank was conducted. A set of sub-predictor variables under four main predictor variables namely financial indicators, demographic Indicators, employment indicators, and behavioural indicators was rated based on the perception of the four experts. The results reveal that, based on the experts’ perception, the number of payments per year and payment interval, the loan or credit history, total income, total debt, the checking accounts, and age are the six most influential predictor variables while race, gender, and social status are the three least influential predictor variables.