Zakat and Tax Compliance Behaviour in Yemen: A Conceptual Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arbms.19.1.114Keywords:
Tax, compliance behaviour, zakat payment, YemenAbstract
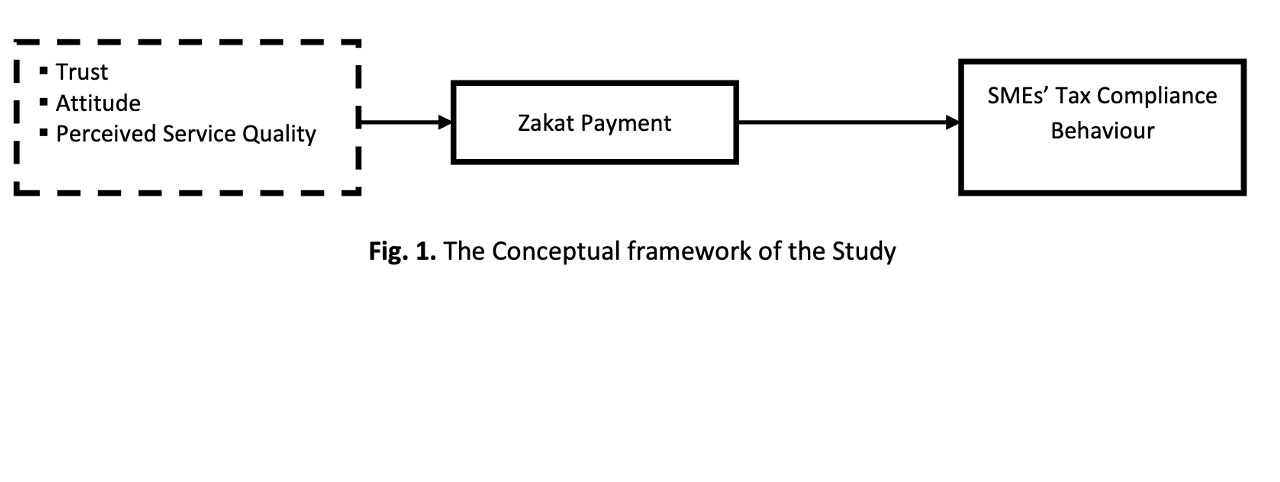
Zakat and tax revenues are important sources of income for financing public activities in many Muslim nations, including Yemen. However, the lack of tax compliance is undermining government efforts to raise the required revenue from these two critical sources, especially in Yemen. In Yemen, paying zakat to the government is a compulsory obligation for both individuals and corporate entities, and the same applies to conventional tax. Therefore, individuals and business establishments are reluctant as they consider paying both zakat and tax as double taxation on their income. Others perceive the way and manner by which zakat is imposed, collected, administered, and distributed, as unfair, which also causes dissatisfaction among the taxpayers. They therefore decide not to pay their zakat to the instituted authority. In light of this, the objectives of this study are: (i) to examine the different perspectives of Muslim scholars on conventional tax and zakat; and (ii) to examine previous findings on the effect of zakat and tax payment compliance behaviour of individual and corporate entities. To achieve the study’s objectives, trust, attitude, and perceived service quality, are deemed as among the most influential determinants of zakat payment compliance behaviour among individuals and corporate entities. This study may have practical implications for the Yemeni government in terms of understanding the determinants of zakat and tax payment compliance behaviour of individuals and corporate entities. We recommend that future studies should empirically investigate the proposed concepts to determine the relationships between the determinants and tax compliance behaviour.