Auditor Brand Name and Financial Reporting Fraud of Listed Companies in Nigeria
Keywords:
Big4, earnings management, financial reporting fraud, auditor brand nameAbstract
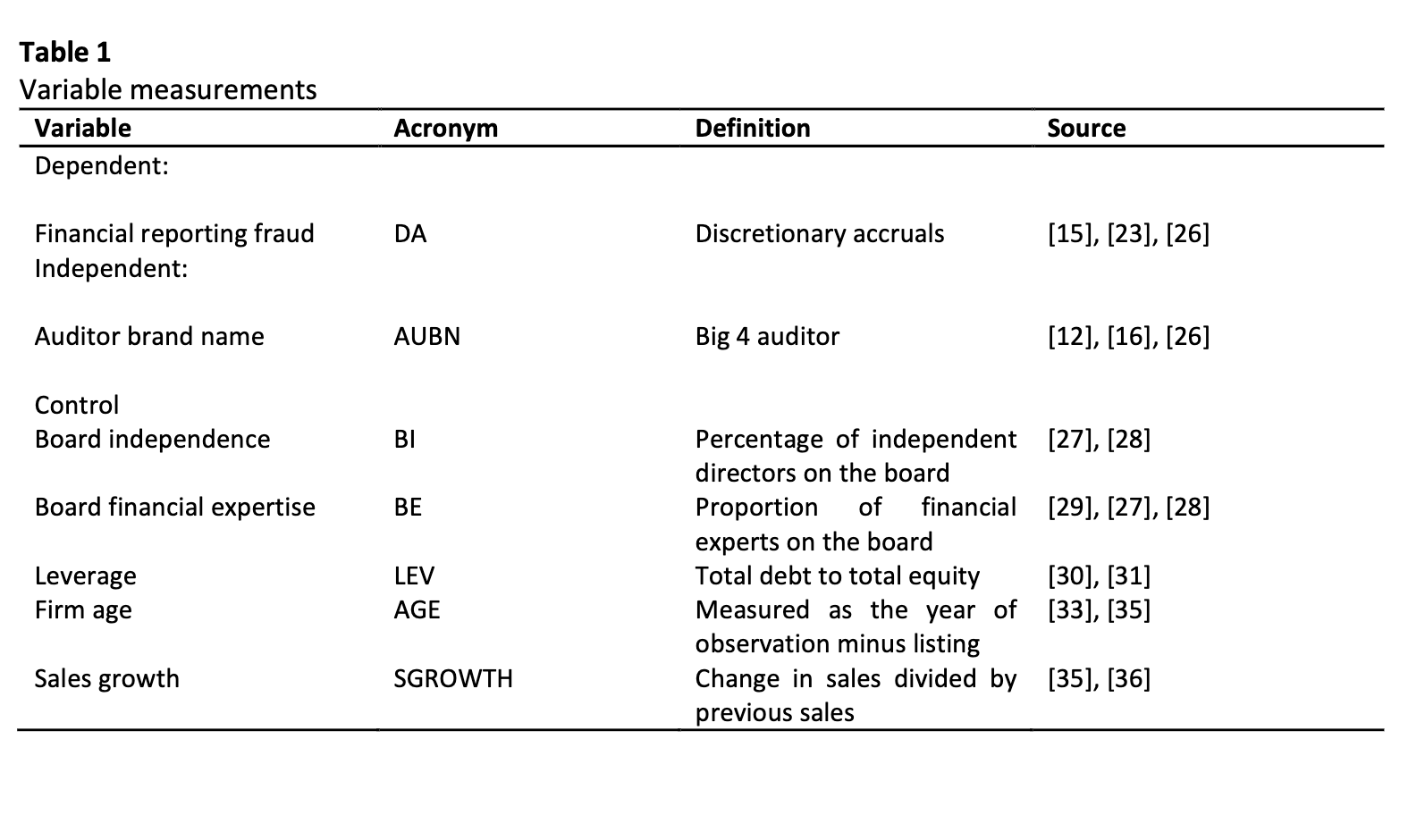
This paper examines the influence of auditor brand name proxied by the Big4 auditors on financial reporting fraud represented by discretionary accruals (DA). We employ 88 listed companies in Nigeria through 440 firm-year observations for the period of five years from 2012 to 2016. The data for the study are extracted from the annual reports of the listed companies and Thompson Reuters DataStream. We adopt accruals model to proxy for financial reporting fraud. Multiple regression is used to estimate the model of the study. After controlling for monitoring and firm-specific attributes, we find that non-Big4 auditors are more likely to detect financial fraud as they might have more excellent knowledge of local markets and better relations with their clients. Consistent with the resource dependence theory, we find that a high proportion of financial experts on the board reduces the extent of financial reporting fraud, thus leading to better financial reporting quality. The study informs regulators and policymakers on the importance of auditor brand name in curtailing financial reporting fraud in the listed companies of Nigeria. The findings are robust to the alternative estimation. The results contribute to the debate on the role of auditor brand name in curtailing financial reporting fraud.