Tax Incentives and Industrial/Economic Growth of SubSaharan African States
Keywords:
fiscal policy, industrial growth, revenue, tax and tax incentives, economic growthAbstract
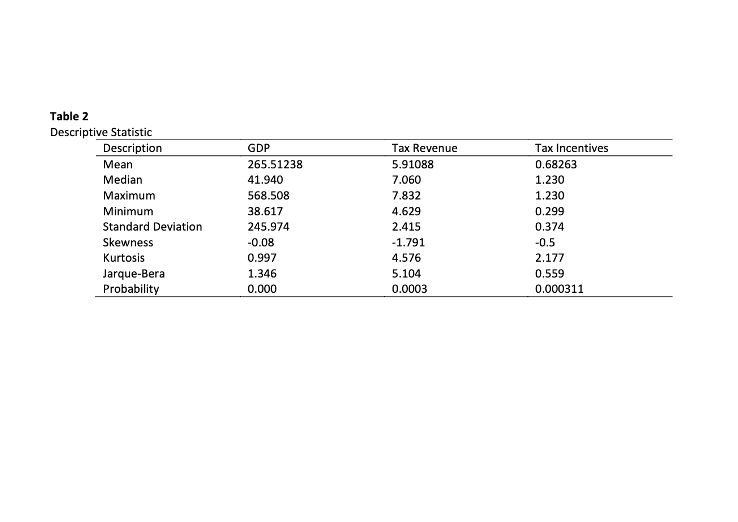
This study investigated the impact of tax incentives on industrial growth of Sub-Sahara African States using Nigeria and Ghana as case studies. Data were obtained from World Bank Data Index (WDI), Federal Inland Revenue Services (FIRS), Ghana Revenue Authority (GRA), Nigerian Investment Promotion Commission (NIPC), Ghana Investment Promotion Centre (GIPC) and Action-aid International (AAI) for 4-year period between 2011 and 2014. A linear model of Tax Revenue, Tax Incentives and Economic Growth, proxied by GDP, was estimated using the Ordinary Least Square technique. The result indicated a 0.529:1 relationship between tax incentives and GDP, which show that Africa is not doing much at the moment to encourage productivity. The result, amongst others, indicate positive effect of tax incentives on industrial and economic growth, suggesting that increasing tax incentives to productive and priority sectors of African economy will increase the continent’s gross domestic products. It was therefore recommended that Sub-Sahara African States should grant more incentives to those sectors and monitor closely the administration of such incentives through special parastatals so as to generating relevant financial data of the actual amount of incentives relative to the economic growth regularly to evaluate the efficiency of tax incentives in the economy