Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Analysis of Different Sizes of Savonius Rotor Wind Turbine
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.94.1.712Keywords:
Savonius Wind turbine, 3D simulations, CFD ANSYS Fluent, Torque coefficient, Power coefficientAbstract
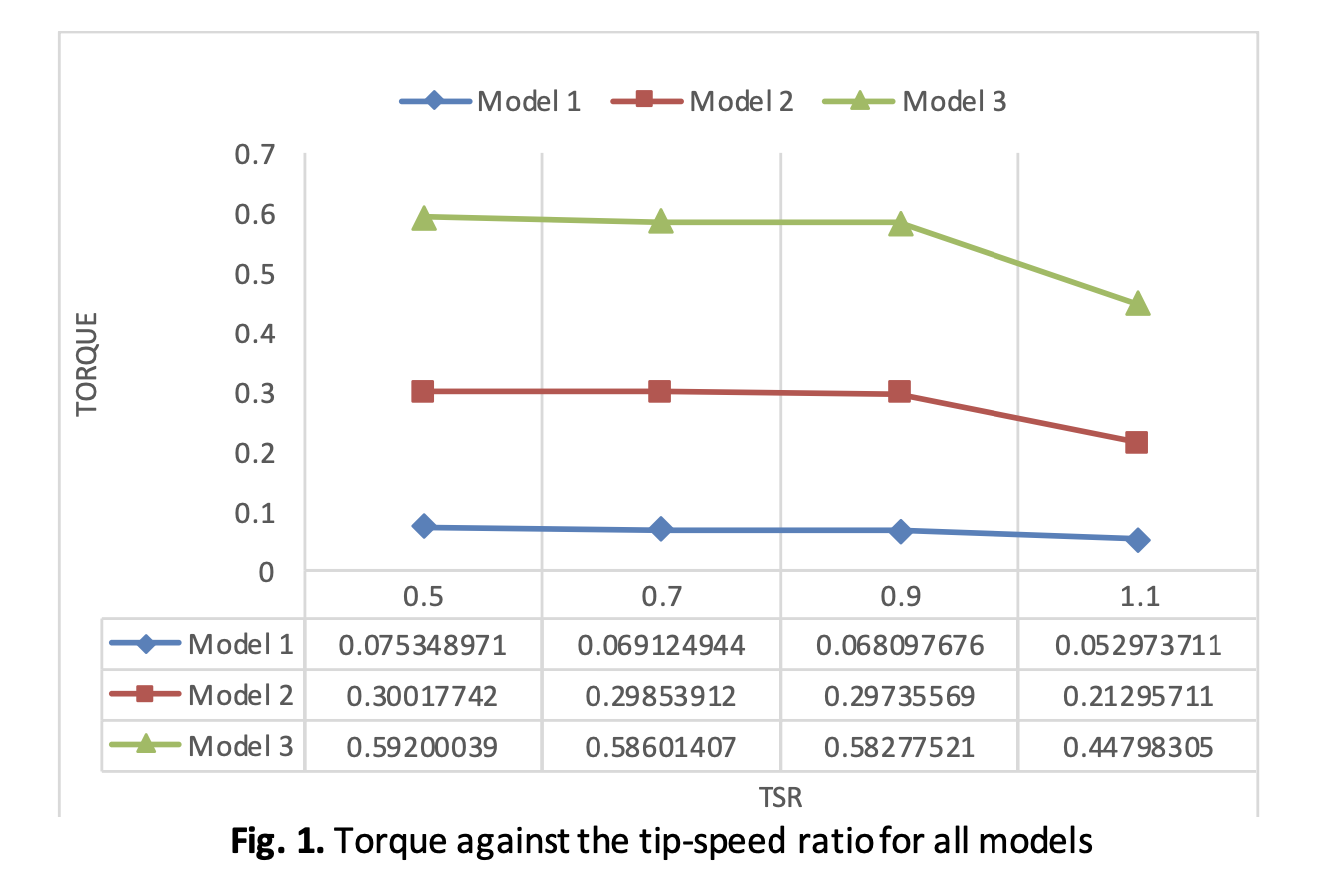
Wind energy is one of many renewable energy sources available. This energy is environmentally friendly green energy. Wind turbines can act as electric generators when the wind passes through them. It's also an alternative to burning fossil fuels or carbon, which can harm the environment in terms of gas emissions. According to the data, wind power is one of the fastest-growing sources of electricity. The primary goal of this study is to evaluate the Savonius Rotor wind turbine's performance in terms of aerodynamic characteristics, including torque, torque coefficient, and power coefficient. The design of Savonius wind turbine blades is the subject of this study. The size of wind turbine blades significantly impacts how efficiently they generate electricity. Ensuring the wind turbine can efficiently work requires the proper selection of blade size for the Savonius wind turbine. The blade modeling used Solidworks 2021 and then generates in Ansys Design Modeler 2021 R1 to define the fluid domain. In addition, a CFD study with three distinct turbine blades is performed using FLUENT 2021 R21. A constant wind speed value of 9.2 m/s has been used throughout the simulation. The simulation was carried out using a transient time flow with a constant upstream wind speed. The results have shown that the power coefficient of all models increases with TSR and the highest efficiency is consensually obtained at almost a unity (0.9) TSR. Comparing the performance of all models, Model 2 generates the highest power coefficient followed by Model 3 and Model 1, respectively. In terms of power, torque and torque coefficient, nearly similar conclusion is drawn.