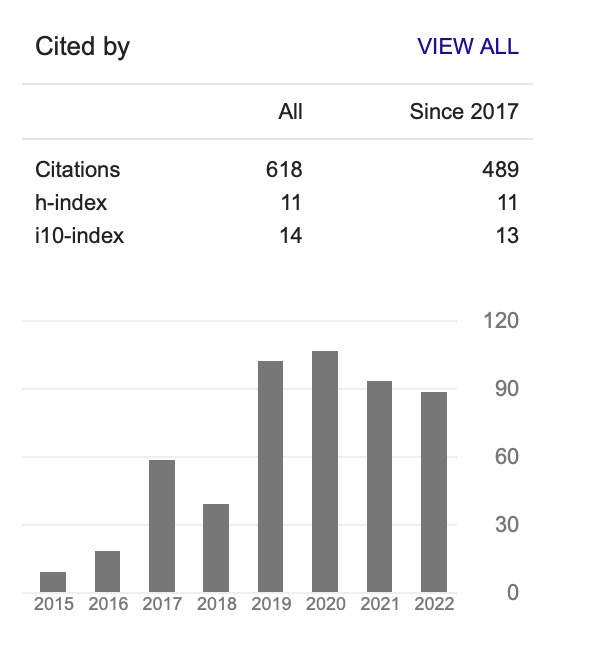
Heat Transfer Enhancement in Straight Channel with Nanofluid In Fully Developed Turbulent Flow
Keywords:
secondary flow, nanofluids, Reynolds numberAbstract
A numerical study for investigating the secondary flow configuration in square straight channel with hydraulic diameter of 0.02m and heat transfer enhancement of water and three different types of nanofluids (Al2O3, TiO2 and CuO) in water as base fluid under constant heat flux in upper and lower walls. The study conducted at steady state, turbulent forced convection and threedimensional flows. Certain boundary conditions and assumptions to solve the governing equations were implemented with using finite volume method. CFD software’s involving GAMBIT and FLUENT were employed to perform the investigation numerically in the range of Reynolds number 104-106. The results show that by increasing Reynolds number the secondary flow increase as well as shear stress is increased, the boundary layers decrease and increase the gradient velocity near a wall. As the volume concentration increases, the wall shear stress and heat transfer rates increase. The three types of nanofluids achieved higher Nusselt number while the friction factor of all of them was seen at similar values. Nanofluid with CuO, nanoparticle achieved the highest Nusselt number followed by TiO2 and Al2O3, respectively while the pure water came last in considered range of Reynolds number. The Nusselt number CuO-water increased with the increase of volume fraction and with the increase of Reynolds number. Reynolds number caused to enhance Nusselt number for all cases. The local Nusselt number for CuO-water increased with increase of Reynolds number.