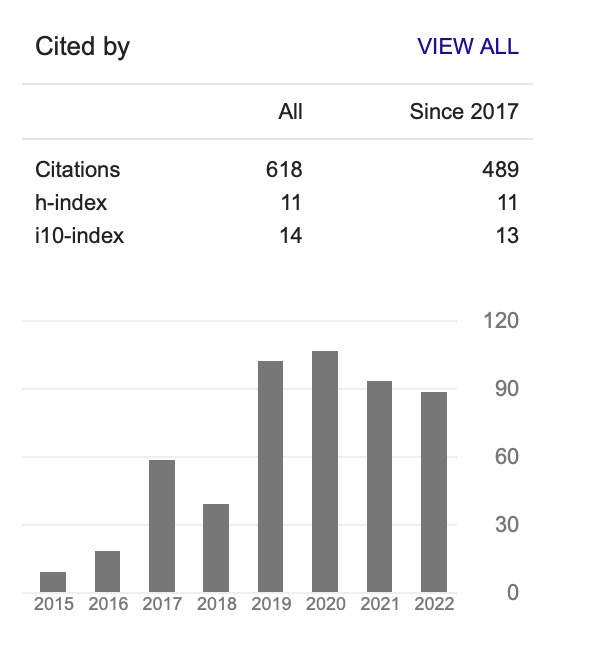
Undergrounds Water Pipe Mapping using Ground Penetrating Radar and Global Positioning System
Keywords:
ground penetrating radar, underground water pipe, 400 MHz frequency antennaAbstract
A complete water pipe plan with the position and depth of the water pipe from ground surface is really important for future maintenance, upgrading and construction. A nondestructive technique, Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) with 400 MHz frequency antenna and Radan 7 software from GSSI can be utilised to detect the buried water pipes under concrete and asphalt pavement and dry clay at more than 1 m from the ground and with the support from global positioning system (GPS). Site tests where the depth of the pipes are accessible from the ground (concrete and asphalt pavements and dry clay) were done to determine the accuracy of the GPR signal analysis. Results shows that the depth of embedded water pipe obtained using GPR under concrete pavement is 1.55 m while the actual depth is 1.64 m with 9 cm or 5% difference and is 0.96 m (GPR) and 1 m (actual) with 4 cm or 4% difference under dry clay. Both results shows that GPR method is accurate with negligible error. The depth of embedded water pipe under asphalt pavement is later determined as 1.2 m. Standard Guideline for Underground Utility Mapping by Department of Survey and Mapping Malaysia (JUPEM) required accuracy of 10 cm (in vertical and horizontal direction) of the utilities mapped to be classified as Quality Level A. Based on results of these site surveys, analysis of GPR electromagnetic waves to map underground utilities is proposed when Quality Level A is required and mapping plan of underground pipe can be produced with help of GPS.