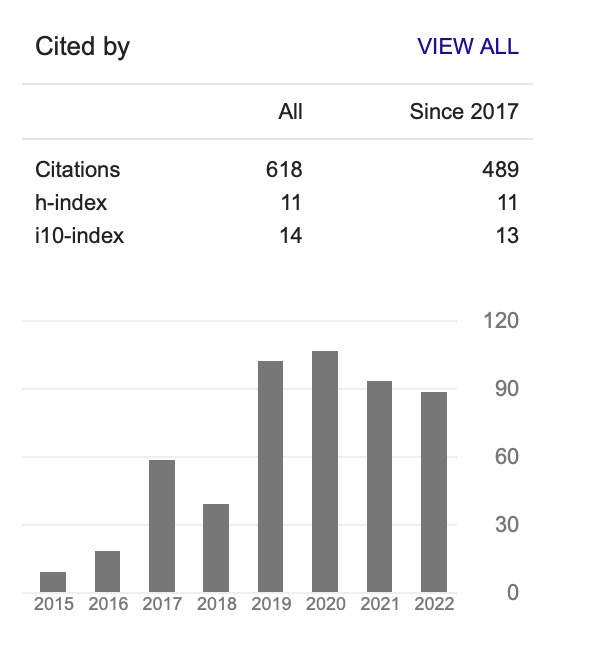
Sustainable Power Generation Pathways in Malaysia: Development of Long-range Scenarios
Keywords:
scenario, long-range, emission, renewable, energy policyAbstract
Power generation in Malaysia significantly depends on three major fossil fuel sources namely coal, natural gas and fuel oil. Burning of these fossil fuels emits greenhouse gases (GHG) into the atmosphere. The usage of fossil fuels for power generation also severely affects the fossil fuel reserves. In the current consumption trends, the reserve for natural gas is projected to be completely diminished by 41 years whereby crude oil by 29 years. As Malaysia is set to be a high-income nation by 2020, electricity demand would also increase furthermore. In this perspective, Malaysia is looking for alternative fuels for electricity generation to deal with the challenges and leading to a sustainable power generation sector. Malaysia is endowed with a huge amount of renewable energy resources and these could be the potential alternative for power generation. Application of renewable resources also results in several technical, financial and policy implications. Scenario building can assist policy makers to understand their implications and enable them to enact relevant measures. The purpose of this work is to develop a few power generation scenarios with various fossil and renewable resource shares for Malaysia. Three alternative scenarios, i.e. Maximum Renewable Energy Scenario, 50% renewable share by 2050 scenario, and Optimistic Energy Scenario were built based on latest information on renewable resources and energy efficiency technologies. Simulation software called Long-range Energy Alternative Planning (LEAP) system was utilized to projecting those alternative scenarios from 2015 onwards. This work found that these three alternative scenarios provide sufficient power supply and keep emissions within target limit. Policy makers can gain insights from these alternative scenarios and enact necessary policy measures to counteract the emission and fossil fuel depletion challenges.